As a narrowband IoT technology, NB-IoT stands out in various industries and its applications cover many fields. So, this article will explain the main application categories and related characteristics of NB-IoT.


1. What is NB-IoT?
NB-IoT refers to Narrow Band -Internet of Things (Narrow Band-Internet of Things) technology. NB-IoT focuses on the Low Power Wide Coverage (LPWA) Internet of Things (IoT) market and is an emerging technology that can be widely used around the world. NB-IoT uses License frequency bands and can be deployed in three ways: in-band, guard band or independent carrier to coexist with existing networks.
2. NB-IoT has four major characteristics
High coverage: NB-IoT has strong indoor coverage, with a gain 20dB higher than LTE, which is equivalent to a 100-fold improvement in coverage area capabilities. It can not only meet the wide coverage needs in rural areas, but is also suitable for applications that require deep coverage such as factories, underground garages, and manhole covers. Take manhole cover monitoring as an example. In the past, the GPRS method required extending an antenna, which was easily damaged by vehicles. However, NB-IoT can solve this problem well as long as it is deployed properly.
Strong link: With the same base station, NB-IoT can provide 50 to 100 times the number of access points than existing wireless technologies. One sector can support 100,000 connections, supporting low latency sensitivity, ultra-low equipment cost, low equipment power consumption and optimized network architecture. For example, due to bandwidth limitations, operators only open 8 to 16 access points for each router in the home, and there are often multiple mobile phones, laptops, and tablets in a home. Hundreds of sensing devices need to be connected to the Internet, which has become a thorny problem. NB-IoT is enough to easily meet the networking needs of a large number of devices in future smart homes.
Low power consumption: Low power consumption is an important indicator for Internet of Things applications, especially for some devices and occasions where batteries cannot be replaced frequently, such as various sensing and monitoring equipment placed in remote areas of high mountains and wilderness. They cannot be as smart as The mobile phone needs to be charged once a day, and the battery life of several years is the most essential requirement. NB-IoT focuses on small data volume and low-speed applications, so the power consumption of NB-IoT devices can be very small, and the device life can be greatly increased from the past few months to several years.
Low cost: Compared with LoRa , NB-IoT does not need to re-establish the network, and the radio frequency and antenna are basically reused. Taking China Mobile as an example, there is a relatively wide frequency band in 900MHZ. It only needs to clear part of the 2G frequency band to directly deploy LTE and NB-IoT simultaneously. Low speed, low power consumption, and low bandwidth also bring low-cost advantages to NB-IoT chips and modules. Modules are expected to cost no more than $5.
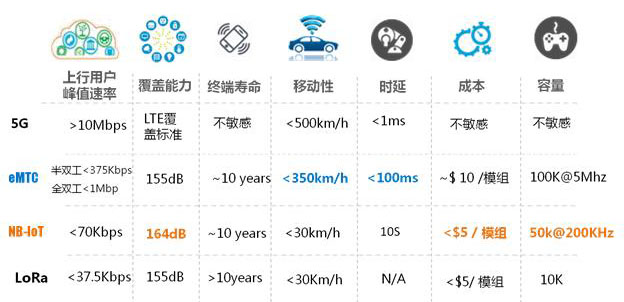

Comparison of NB-IoT and other LPWA technologies
3. Main application categories of NB-IoT
In the field of low-speed Internet of Things, NB-IoT, as a new standard, achieves the ultimate in cost, coverage, power consumption, number of connections and other technologies. This technology is widely used in eight typical industries including public utilities, consumers, medical and health, smart buildings, smart cities, agricultural environment, logistics and warehousing, and manufacturing industries.
Utilities: meter reading (water/gas/electricity/heat), smart water services (pipe network/leakage/quality inspection), smart fire extinguishers/fire hydrants.
Consumers: wearable devices, bicycle/motor vehicle anti-theft, smart luggage, VIP tracking (children/elderly/pets/vehicle rental), payment/POS machines.
Medical health: drug traceability, remote medical monitoring, blood pressure monitors, blood glucose meters, and heart armor monitoring.
Smart buildings: access control, smart HVAC, smoke/fire alarm detection, elevator failure/maintenance.
Smart city: smart street lights, smart parking, urban trash can management, public safety/alarm, construction site/urban water level monitoring.
Agricultural environment: precision planting (environmental parameters: water/temperature/light/medicine/fertilizer), livestock breeding (health/tracking), aquaculture, food safety traceability, urban environment monitoring (water pollution/noise/air quality PM2.5) .
Logistics and warehousing: asset/container tracking, warehousing management, fleet management/tracking, cold chain logistics (status/tracking).
Manufacturing industry: production/equipment status monitoring, energy facilities/oil and gas monitoring, chemical park monitoring, large rental equipment, predictive maintenance (home appliances, machinery, etc.).
NB-IoT is an emerging Internet of Things technology that has attracted much attention due to its low power consumption, stable connection, low cost, and excellent architecture optimization. As NB-IoT technology becomes more mature, it will appear in more fields. .