The number of Internet of Things connections has grown significantly in the past year. Currently, various wireless connection technologies on the market are advancing hand in hand, and no one has a dominant advantage. With the rise of LPWAN technology and 5G, the development speed of the Internet of Things will be Become more rapid.


The IoT market experienced an unexpected acceleration in Q1/Q2 2018, with the total number of IoT devices in use reaching 7 billion connections.
The related performance of IoT companies is also growing rapidly, especially IoT software, cloud computing and service companies, which have far exceeded revenue expectations. Sales of Microsoft Azure and Amazon AWS grew by 93% and 49% respectively in the past 12 months, with the IoT segment contributing significantly to growth. Even IoT innovators like C3IoT have seen their revenue grow by 60% this year.
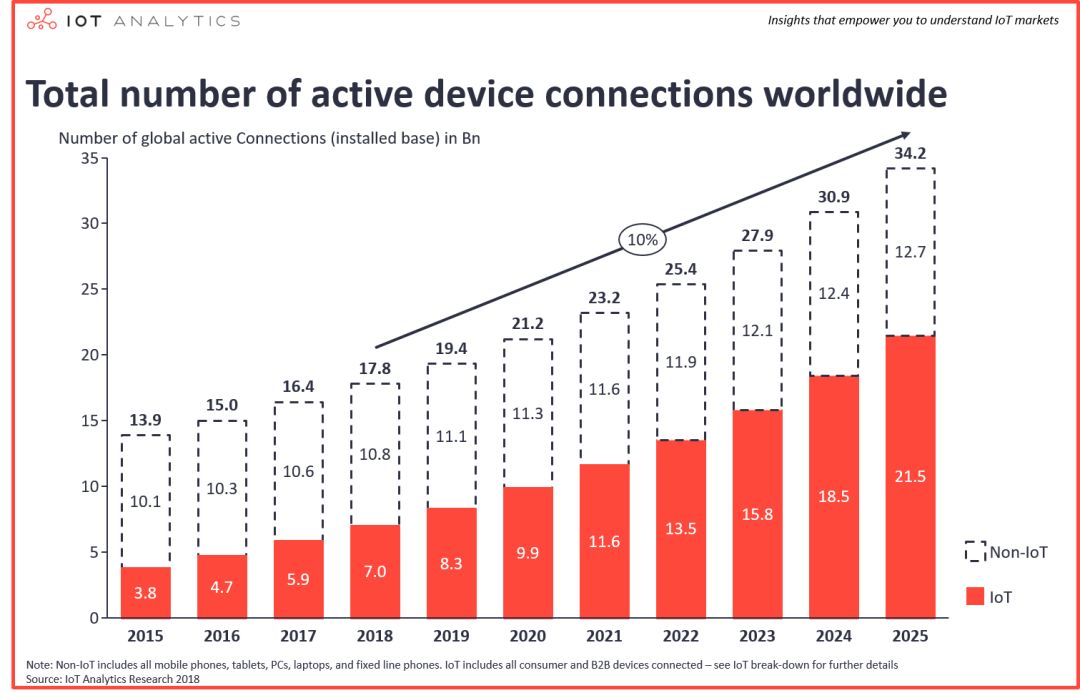
The number of connected devices worldwide has reached 17 billion
At present, the number of Internet-connected devices in the world has exceeded 17 billion. Excluding connections such as smartphones, tablets, laptops or landline phones, the number of IoT devices has reached 7 billion.

Global distribution of the number of connected devices
The number of IoT devices worldwide is 7 billion
The growth in the number of global connections is mainly due to the strong growth of IoT devices, both on the consumer side (smart homes, smart hardware, etc.), and enterprise-level connections (machine devices, etc.) have gained strength in recent time periods growth of. The number of active IoT devices is expected to increase to 10 billion by 2020 and 22 billion by 2025.
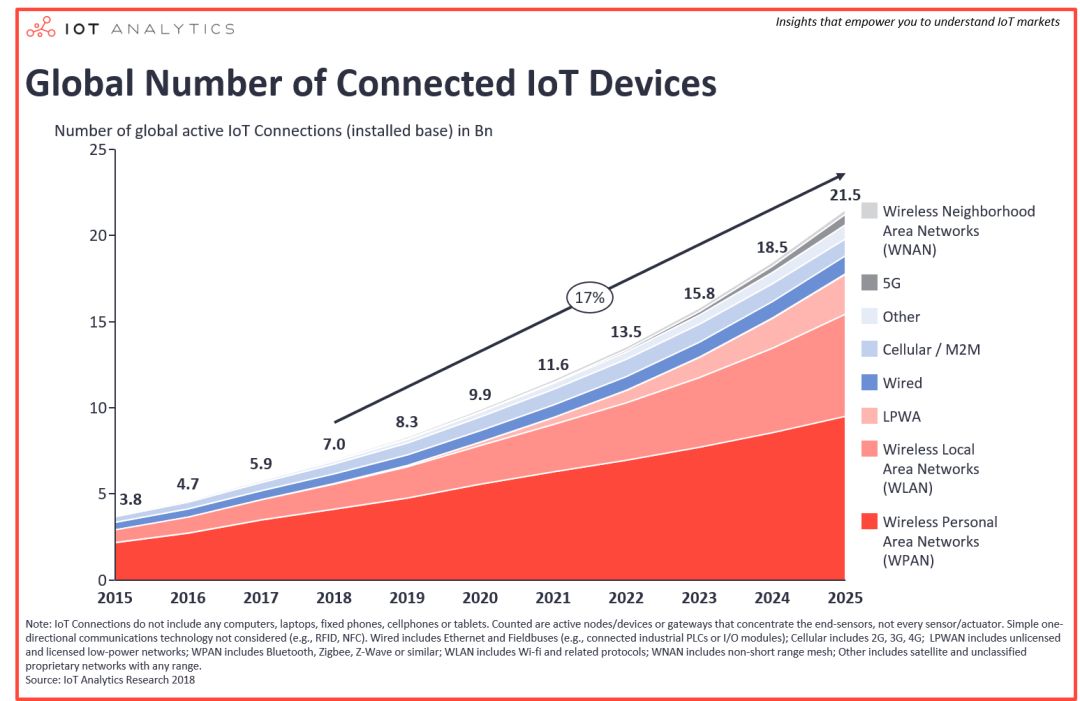

Connection volumes for different connection technologies
Short range private wireless network
Among many connection technologies, short-range wireless technology connects the largest number of IoT devices, and the maximum distance for such applications usually does not exceed 100 meters. Including Bluetooth, Zigbee and Z-wave connected devices, most of these devices are used in consumer applications such as smart homes, such as connecting smoke alarms or thermostats.
Drahtloses LAN
Another big category is wireless LAN. This type of application usually requires local area networking applications within a range of about 1 kilometer. WIFI is one of the most common technologies, and in the next few years, this type of scenario will maintain a high growth rate. At present, it is mainly used in home intelligent scenarios, such as smart TVs and smart speakers, and it is also increasingly used in industrial production.
LPWAN
A large portion of future growth in the number of IoT devices is expected to come from low-power, wide-area networks. By 2025, the number of devices connected via LPWAN is expected to exceed 2 billion. This technology guarantees extremely high battery life and a maximum communication distance of more than 20 kilometers. There are three main LPWAN technologies, namely Sigfox, Lora and NB-IoT. Currently, Sigfox, Lora and NB-IoT have launched more than 25 million devices worldwide, most of which are smart meter reading applications.
Wired connection
When people think of the Internet of Things, few think of wired connections. However, in many cases, wired device connections are still the cheapest and most reliable option. Especially in industrial environments, both fieldbus and Ethernet technologies are using wired connections and are expected to continue to do so in the coming years.
Cellular/M2M
2G, 3G and 4G technologies have long been the only options for remote device connectivity. As LPWAN and 5G technologies develop, these traditional cellular technologies are expected to lose market share as LPWAN and 5G offer more cost-effective solutions.
5G
5G technology, still in the development stage in 2018, is expected to usher in a new era of connectivity through its massive bandwidth and extremely low latency, and is now being vigorously promoted by governments, especially the Chinese government. The Chinese government will regard 5G as an important social asset and national strategy, aiming to transfer technological innovation from the United States and Europe to China.
In the United States, the first prefabricated 5G networks will provide fixed wireless access to residential and small business customers by the end of the year. There will be more applications when the final standard is approved in 2020.
other
Other technologies such as satellite and proprietary networks will continue to play a role in the IoT, albeit with a smaller market share, but are also among the technologies that enrich the IoT.
The global IoT market reached US$151 billion in 2018 and is expected to increase to US$1,567 billion by 2025
The current market sentiment and short-term prospects for IoT are extremely optimistic. As more data is moved to the cloud, new IoT applications are introduced to the market, and the importance of analyzing data continues to increase, software and platforms are expected to continue to drive the market.
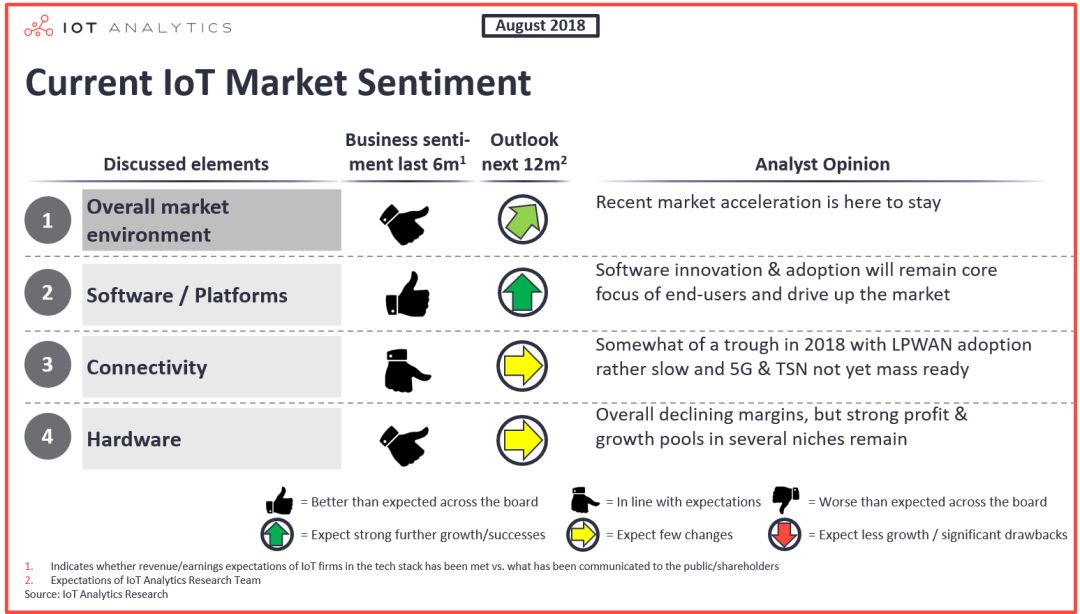

In the past year, the number of IoT hardware connections has maintained steady growth, but due to the increase in volume, the profit margin of the entire industry has also declined. Since LPWAN technology has just been launched to the global market and 5G has not yet been put into large-scale use, it is expected that in 2019 or even later, the IoT connection technology market will maintain a situation where various technologies are advancing hand in hand.
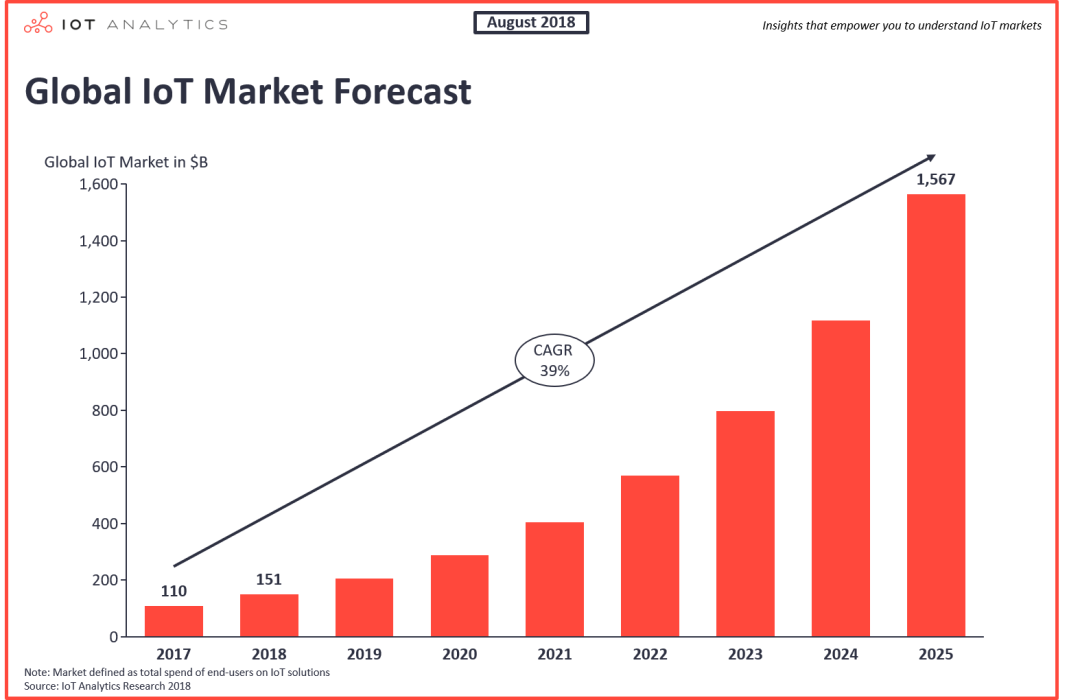

Global IoT market spending is expected to grow 37% in 2017 to $151 billion. Due to the market acceleration of IoT (as noted in the chart above), these estimates have been revised upward, and the market is now expected to total $1,567 billion by 2025.
Current IoT market trends
The current market environment of the Internet of Things is changing dynamically, and there are many angles to analyze the future market forecast. For example, one trend among Internet of Things cloud platform suppliers is not only to provide simple software services, but also to provide packaged hardware. Middleware allows users to better connect with the platform to improve interoperability and performance between IoT devices and data stored and analyzed in public or private clouds. Microsoft, Amazon and Google have all recently announced their own hardware. It remains to be seen whether these shifts from the cloud to hardware will pose a threat to some of the existing hardware vendors, such as gateway providers or chipmakers.
In fact, it is not just the hardware development of cloud computing companies. More and more Internet of Things companies are expanding their product and solution lines. They are no longer a single product or a single technology supplier, but provide a A complete solution.
In addition, due to the fragmentation and mobility of IoT scenarios, more and more products have more requirements for the “non-technical indicator” of size, because IoT products will integrate more components and component sizes. The smaller it is, the better it is in terms of space saving and ease of use.
The transformation of the Internet of Things into wireless has also placed higher requirements on the low-power consumption indicators of communication technology and display technology. This is also the reason why LPWAN network technology has become so popular in recent years. Of course, in addition to optimizing the energy consumption technology, In addition, the improvement of battery life is also a breakthrough point. Electric vehicle meter companies including Tesla have made breakthroughs in battery technology as a core technology. Although it is difficult, the benefits it can bring are also very considerable.