LoRa must be familiar to everyone. It is an ultra-long-distance wireless transmission scheme based on spread spectrum technology developed by the American company Semtech. Because of its unique modulation method, it has special features of low power consumption, long distance and high flexibility. , so it is named “LoRa” (Long Range, meaning long distance).
Currently, LoRa mainly operates in free frequency bands around the world, including 433, 868, 915 MHz, etc. In addition, we also need to understand the concepts related to LoRa. Today we will talk about “those things” about LoRa
LoRa modulation
From a technical perspective, LoRa is a modulation technology that provides longer communication distance than similar technologies. Modulation is based on spread spectrum technology, a variant of linear modulation spread spectrum (CSS), with forward error correction (FEC).
LoRa significantly improves the sensitivity, and like other spread spectrum technologies, uses the entire channel bandwidth to broadcast a signal, making it more robust to channel noise and frequency offsets caused by the use of low-cost crystal oscillators.
LoRa puede modular la señal a 19,5 dB por debajo del ruido de fondo, mientras que la mayoría de los sistemas de modulación por desplazamiento de frecuencia (FSK) requieren una potencia de señal de 8-10 dB por encima del ruido de fondo para modular correctamente. La modulación LoRa es la capa física (PHY) y puede ser utilizada por diferentes protocolos y diferentes arquitecturas de red - Mesh, Star, Point-to-Point, etc.
LoRaWAN
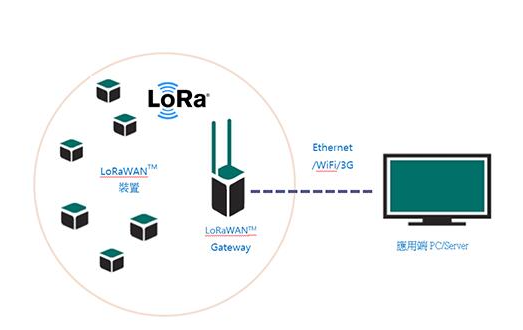
The difference between LoRa and LoRaWAN is that LoRa modulation is PHY, while LoRaWAN is a MAC protocol, which is used for large-capacity, long-distance, low-power star networks. The LoRa Alliance is standardizing low-power wide area networks (LPWAN).
The LoRaWAN protocol is optimized for low-power, battery-powered sensors and includes different levels of end nodes to optimize the balance between network latency and battery life. It’s completely bi-directional and built by security experts to ensure reliability and security.
The LoRaWAN architecture also makes it easy to locate mobile targets for asset tracking, which is the fastest growing application in the Internet of Things. Major telecom operators are deploying LoRaWAN as a national network, and the LoRa Alliance is standardizing LoRaWAN to ensure that different national networks are interoperable.
Pasarela LoRa
The LoRa gateway is designed for long-distance star architecture and is used in the LoRaWAN system. It has multi-channel, multi-modulation transceiver, and can demodulate multiple channels at the same time. Due to the characteristics of LoRa, it can also demodulate multiple signals on the same channel at the same time.
The gateway uses RF equipment different from the end node, has higher capacity, and acts as a transparent bridge to relay information between the end device and the central network server. The gateway connects to the network server through a standard IP connection, and the terminal device uses single-hop wireless communication to one or more gateways.
Communication between all terminal nodes is generally two-way, but also supports multicast function operations, software upgrades, wireless transmission or other mass release of information, thus reducing wireless communication time. There are different gateway versions based on required capacity and installation location (home or tower).
LoRa concentrator
Se utilizan los términos pasarela y concentrador, pero son componentes equivalentes en el sistema LoRa. En otros sectores, las definiciones de pasarela y concentrador significan componentes diferentes.
LoRa anti-interference ability
The LoRa modem suppresses co-channel GMSK interference up to 19.5dB, or in other words, it can tolerate signals 19.5dB below the interfering signal or noise floor.
Because of its strong anti-interference performance, the LoRaTM modulation system can not only be used in frequency bands with high spectrum utilization, but can also be applied to hybrid communication networks to expand coverage when certain modulation schemes in the network fail.
LoRa data rate
LoRaWAN defines a specific set of data rates, but there are many options for the end chip or PHY. The SX1272 supports data rates from 0.3 to 37.5kbps, and the SX1276 supports 0.018 to 37.5kbps.
LoRa end node
LoRa end nodes are parts of the LoRa network that perform sensing or control. They are battery powered over long distances. These end nodes use the LoRaWAN network protocol to establish communication with the LoRa gateway (concentrator or base station).
Auto-Adaptive Data Rate (ADR)
ADR is a method that changes the actual data rate to ensure reliable packet delivery, optimal network performance, and capacity planning.
For example, nodes closer to the gateway use higher data rates (shorter transmission times) and lower output power. Only use the lowest data rate and maximum output power at nodes where the link budget is very marginal.
ADR methods can adapt to changes in network infrastructure and support changing path losses. To maximize the battery life of end devices and overall network capacity, the LoRa network infrastructure manages the data rate and RF output of each end device separately by implementing ADR.
LoRa has quickly been recognized by the market for its low power consumption, long distance and high flexibility. Many of Ebyte’s representative products are based on LoRa spread spectrum technology. In order to further reduce related costs, Ebyte also Launching a new generation of LoRa plan with higher cost performance, welcome new and old friends to buy!Keywords: network IO controller