What is a serial port communication protocol? There are several common ones.
2020-08-11 17:55:30 Zongheng Control Inteligente 5
What is a serial communication protocol? In layman’s terms: it is the protocol transmission method used in serial communication. The explanation in professional terms is: the data sent by serial port one is sent to serial port two, and both of them adopt a specific data packet format before they can be sent and received. If they all use the RS232 protocol, then they can send and receive data between them. This is the serial communication protocol.
There are several serial communication protocols
Before talking about several common communication protocols for serial ports, we need to know that serial communication protocols include internal communication system protocols and inter-system protocols. So let’s explain them one by one below.
Internal system protocols: Common ones include CAN protocol, I2C protocol, and SPI protocol
Inter-system protocols: Common ones include USART protocol, UART protocol, and USB protocol.
What is an internal system protocol? An internal system protocol is used to communicate between two devices on the board. While using these in-system protocols we will extend the peripherals of the microcontroller without using the in-system protocols. Using in-system protocols increases circuit complexity and power consumption. Using in-system protocols, circuit complexity and power consumption are reduced, costs are reduced, and access to data is very secure.
What is an intersystem protocol? An intersystem protocol used to communicate between two different devices. Just like the communication between the computer and the microcontroller kit. Communication takes place via the internal bus system.
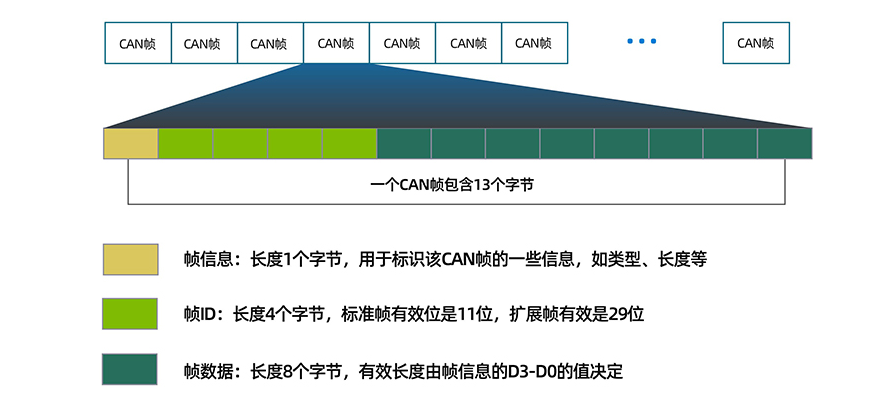
CAN protocol
CAN stands for Controller Area Network. It is a serial communication protocol. It requires two lines CAN high (H) and CAN low (H-). It was developed by Robert Bosh Corporation in 1985 for use in automotive networks. It is based on a message-oriented transport protocol.
The CAN protocol is commonly used in electronic networks in automobiles, aircraft and medical systems. Common products include Can to Ethernet equipment USR-CANET200
The 1970s was the era when car manufacturers started introducing new features such as anti-lock braking, air conditioning, gear control, centrally operated door locks, etc. These features ensure additional wiring and complex designs, increasing costs and risks. To overcome these problems, Robert Bosch introduced the CAN protocol in the 1980s. This serial communication protocol was further standardized as ISO11898 in 1993. It is the CAN protocol that has completely transformed communication between advanced sensors.
I2C protocol
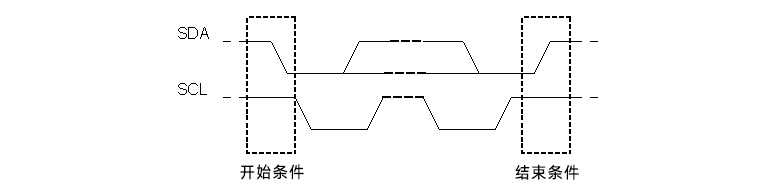
The I2C bus was developed by Philips Semiconductors. Its original purpose was to provide an easy way to connect the CPU to peripheral chips. Peripherals in embedded systems are often connected to the microcontroller as memory mapped devices. I2C requires only two wires to connect all peripherals to the microcontroller. These active lines, called SDA and SCL, are bidirectional. The SDA line is the serial data line, while the SCA line is the serial clock line.
I2C stands for Inter Integrated Circuit. I2C requires only two wires to connect all peripherals to the microcontroller. I2C requires only two wires, SDA (serial data line) and SCL (serial clock line), to transfer information between devices. It is the master of the slave communication protocol. Each slave has a unique address. The master device sends the address and read/write flags of the target slave device. This address matches any slave device that is turned on, the remaining slave devices are in disabled mode. Once the addresses match, communication takes place between the master and that slave, and data is sent and received. The transmitter sends 8 bits of data and the receiver replies with 1 bit of confirmation. After the communication is completed, the master station issues a stop condition.
SPI protocol
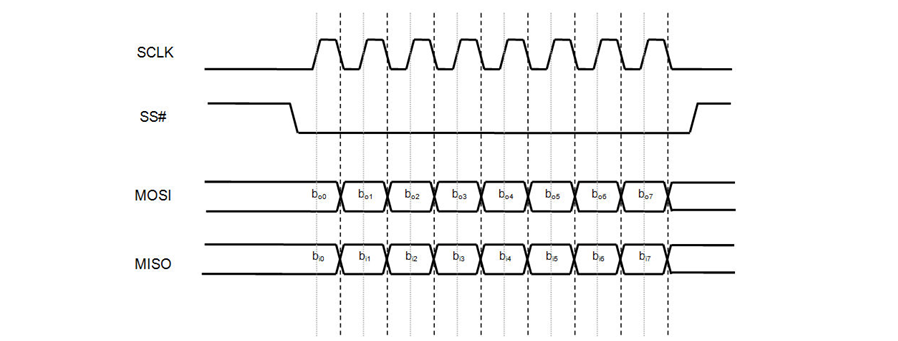
SPI stands for Serial Peripheral Interface. It is one of the serial communication protocols developed by Motorola. Sometimes the SPI protocol is also called a 4-wire protocol. It requires four wires MOSI, MISO, SS and SCLK.SPI protocol is used to communicate master and slave devices. The host first configures the clock with frequency. The host then selects a specific slave device to communicate with via a pull-tab button. Select that specific device and start communication between the master and that specific slave. The master selects only one slave at a time. It is a full-duplex communication protocol. In the case of bit transfers, it is not limited to 8-bit words.
USART protocol
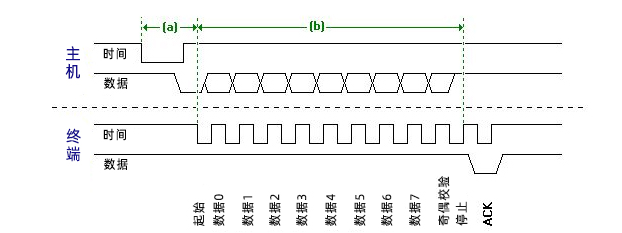
USART stands for Universal Synchronous and Asynchronous Transmitter and Receiver. It is a serial communication of two-wire protocol. Data cable signal lines are labeled Rx and TX. This protocol is used to send and receive data byte by byte along with clock pulses. This is a full-duplex protocol, meaning data is sent and received simultaneously at different board speeds. Different devices communicate with the microcontroller through this protocol. For example, telecommunications.
UART protocol
UART stands for Universal Asynchronous Transmitter and Receiver. The UART protocol is a serial communication with two wired protocols. Data cable signal lines are labeled Rx and Tx. Serial communication is commonly used to send and receive signals. It is transmitted and communicated with the serial port to receive data without pulse-like. The UART receives the data bytes and sends the individual bits sequentially.
USAT protocol is usually used as a peripheral of MCU in embedded systems; generally speaking, the TTL level is directly derived from the chip pin; and the RS232 level may be connected to the conversion chip in the middle.For details, please see: Standards for Serial Communication
UART is a half-duplex protocol. Half-duplex means having the ability to transmit and receive data, but not simultaneously. Most controllers have a hardware UART on the board. It uses a data line to send and receive data. It has a start bit, an 8-bit data and a stop bit, indicating that the 8-bit data is transmitted from high to low. For example: email, text messages, walkie-talkies, industrial IoT transmission equipment serial server.
USB protocol
USB stands for Universal Serial Bus. Again, it is a two-wire protocol for serial communication. Data cable signal wires are marked D and D-. This protocol is used to communicate with system peripherals. The USB protocol is used to send and receive data serially to the host and peripheral devices. USB communication requires driver software based on system capabilities. USB devices can transmit data on the host without any requested bus. Now, most devices today use this technology to communicate with the USB protocol. Use USB to communicate with the ARM controller like a computer. USB transfers data in different modes. The first is a slow mode from 10 kbps to 100 kbps; the second is a full speed mode from 500kbps to 10mbps and a high speed mode from 25mbps to 400Mbps. The maximum USB cable length is 4 meters.
For example: hubs, switches, mice, keyboards, pen drives.
Etiqueta: serial communication protocol
-
What is simplex and full-duplex communication [2020-08-14]
-
What is the DB9 interface [2020-08-14]
-
What is a serial port communication protocol, and there are several common ones [2020-08-11]
- Artículo anterior : What is GPRS DTU and its working principle explained
- Artículo siguiente : What are the functions of RTU?