What is baud rate?
Baud rate refers to the number of data bits transmitted per unit time. It is usually used in serial communication. In serial communication, the sender transmits data to the receiver bit by bit in the form of bits, and the receiver receives these bits at the same rate to complete the data transmission. The higher the baud rate, the faster the data transfer speed.
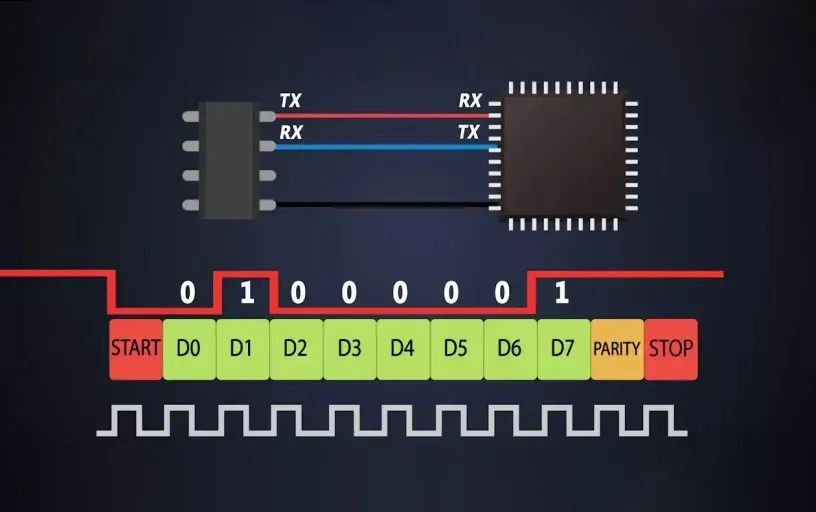
The role of baud rate in serial communication
In serial communication, baud rate plays a vital role. Because when transmitting data, the sender and receiver need to communicate at the same baud rate. If the baud rates at both ends are different, problems such as data loss and transmission errors will occur, resulting in data transmission failure. Therefore, the baud rate is a parameter that must be negotiated in serial communication.
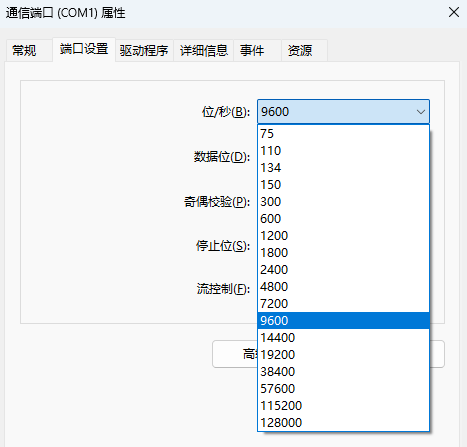
In actual serial communication, common baud rates are 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200, etc. The choice of these baud rates depends on the specific application scenario. For example, if the amount of data to be transmitted is large, you can choose a higher baud rate to increase the transmission rate; if the communication distance is long and the signal attenuation is serious, you can choose a lower baud rate to improve the efficiency of data transmission. reliability.
Important parameters in serial communication
In addition to the baud rate, there are other parameters that need to be negotiated in serial communication, such as data bits, stop bits, parity bits, etc. These parameters also have an important impact on the reliability and rate of data transmission. Let’s introduce the functions of these parameters one by one:
bits de donnéesData bits refer to the number of bits that actually carry data in each data frame. In serial communication, the value of data bits is usually 7 or 8. When the data bits are 7, the number of data bits carried in each data frame is 7; when the data bits are 8, the number of data bits carried in each data frame is 8. The selection of data bits is usually based on the amount of data that needs to be transmitted. If the amount of data that needs to be transmitted is large, larger data bits can be selected. |
Bit d'arrêtThe stop bit refers to the last bit of each data frame. In serial communication, there are usually 1 or 2 stop bits. When the stop bit is 1, there will be one more bit as a stop bit in each data frame; when the stop bit is 2, there will be two more bits as stop bits in each data frame. The selection of stop bits usually depends on the specific application scenario. If the reliability of data transmission needs to be improved, more stop bits can be selected. |
Chiffre de contrôleThe parity bit is designed to detect errors in data transmission. In serial communication, there are usually two methods: parity check, even check and no check. Parity check refers to adding a bit to the last bit of each data frame so that the number of 1’s in the entire data frame is an odd or even number to detect whether there is an error in the data transmission. Even parity means adjusting the number of 1’s to an even number. Without verification, data is transmitted directly without any detection. When selecting parity bits, it is usually necessary to consider the reliability and efficiency of data transmission. If the data to be transmitted is important, you can choose parity to improve the reliability of data transmission; if the data transmission rate is important, you can choose no parity to improve efficiency. |
In addition to the above three parameters, there are some other parameters that need to be paid attention to in serial communication, such as flow control, serial port mode, etc. Flow control refers to the method of controlling data flow during data transmission. There are usually two methods: hardware flow control and software flow control. Serial port mode refers to the way of data transmission in serial port communication. There are usually two types: asynchronous serial port mode and synchronous serial port mode.
Résumer
In general, baud rate is a very important parameter in serial communication. It determines the rate and reliability of data transmission, and also affects the stability and efficiency of serial communication. When performing serial communication, it is necessary to select the appropriate baud rate and other parameters according to the specific application scenario to ensure the success and stability of data transmission.