Requirements overview
This chapter mainly implements a process: EG8200 collects data from Siemens S7-200 Smart, assembles it into JSON format, and reports it to the application platform through MQTT; at the same time, it can receive control commands issued by the application platform to realize remote switching. To implement this process, the following materials need to be prepared in advance:
-
The IP port and point table of the PLC to be collected, for example:
|
PLC |
S7-200 Smart |
||
|
IP |
192.168.0.24/102 |
||
|
Point table (DB1) |
|||
|
address |
type of data |
Attributes |
name |
|
V0.0 |
Boolean |
read only |
No. 1 motor start and stop status |
|
V0.1 |
Boolean |
read only |
No. 2 motor start and stop status |
|
V0.2 |
Boolean |
read only |
No. 3 motor start and stop status |
|
V0.3 |
Boolean |
read only |
No. 4 motor start and stop status |
|
V0.4 |
Boolean |
Read and write |
No. 1 motor start and stop control |
|
V0.5 |
Boolean |
Read and write |
No. 2 motor start and stop control |
|
V0.6 |
Boolean |
Read and write |
No. 3 motor start and stop control |
|
V0.7 |
Boolean |
Read and write |
No. 4 motor start and stop control |
|
VD100 |
Unsigned16 |
read only |
Voltage (V) |
|
VD200 |
Unsigned16 |
read only |
Current (A) |
-
MQTT communication related parameters and JSON data format requirements, such as:
url:1883.dtuip.com:1883clientID:820000003058164Fusername:19381903226password:ZHZK19381903226Subscribe:820000003058164F/ Publish:820000003058164FJSON format:{ "sensorDatas": [ { "fla g":"em1Status", "switcher":1 }, { "flag" :"em2Status", "switcher":1 }, { "flag":"em3Status", "switcher":1 }, { "flag":"em4Status", "switcher":1 }, { "flag":" em1Control", "switcher":0 }, { "flag":"em2Control", "switcher":0 }, { "flag":"em3Control", "switcher":0 }, { "flag":"em4Control" , "switcher":0 }, { "flag":"voltage", "value":220.0 }, { "flag":"current", "value":10.2 } ]}
demand analysis
When making a process, the basic logic is to make the process based on the data trend . After analysis, it can be concluded that this demand is mainly divided into two parts: data uplink and data downlink. Among them, the main tasks of data uplink include:
-
Read PLC data through the S7 protocol, and the obtained data is stored in the memory (
S7节点) -
Format data according to JSON format (
函数节点) -
Establish an MQTT connection and publish to the specified topic (
MQTT发布节点)
The main tasks of data downlink include:
-
Subscribe to MQTT topics and receive data sent by the platform (
MQTT订阅节点) -
Parse the received JSON data and store it in memory (
函数节点) -
Write to the PLC in the format required by S7 (
S7节点)

Requirements realization
1. Collect PLC data
-
Drag an
S7读数据节点and a调试节点from the node library .调试节点is used to view the read PLC data to facilitate problem location.

-
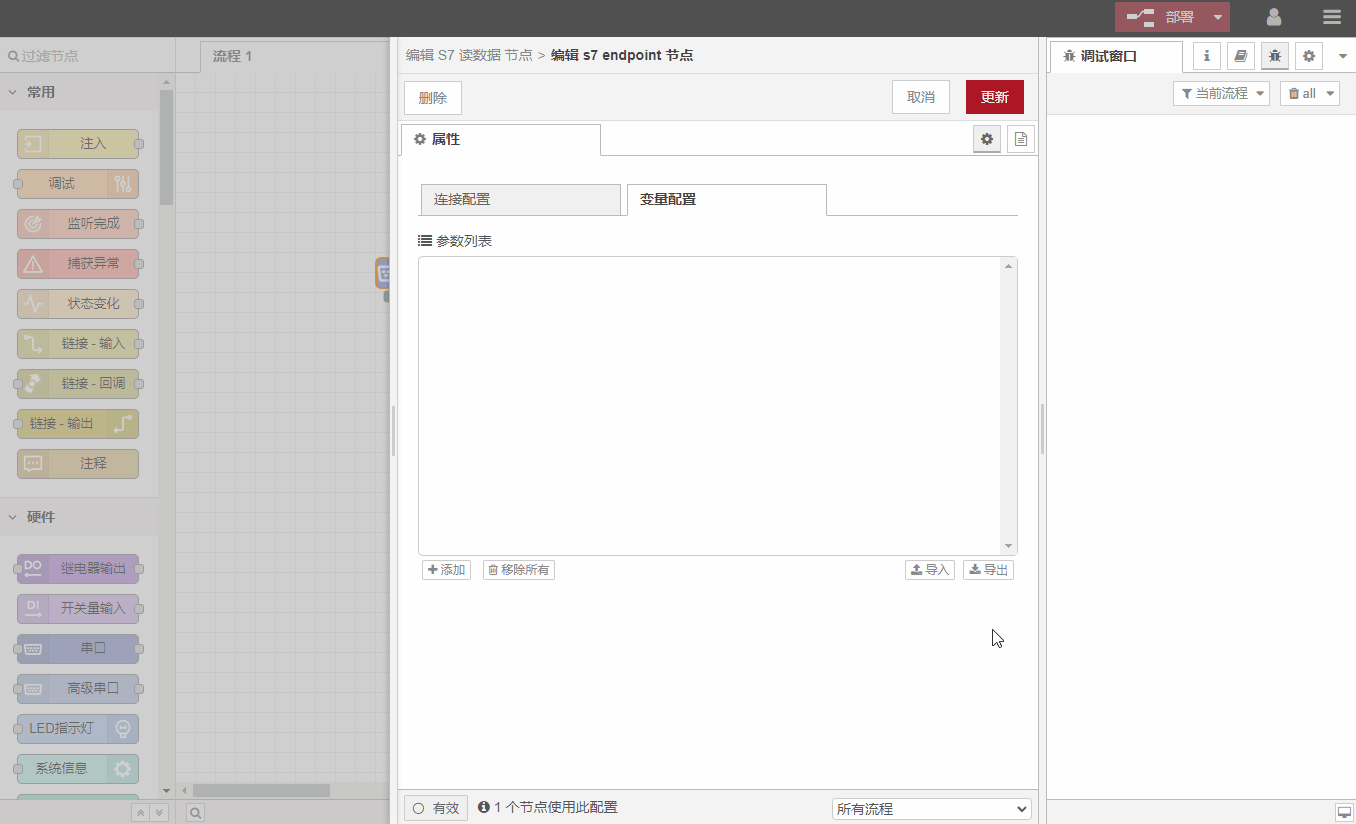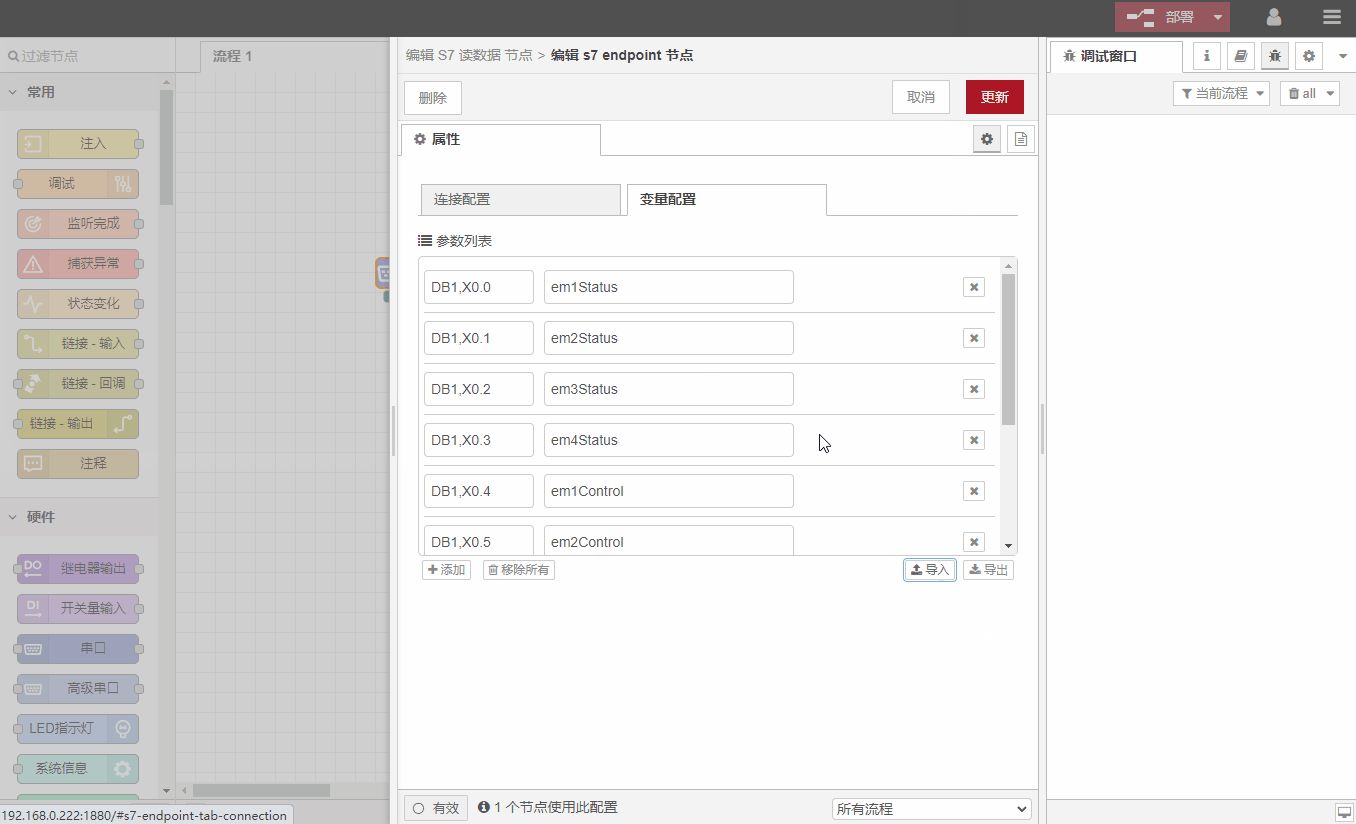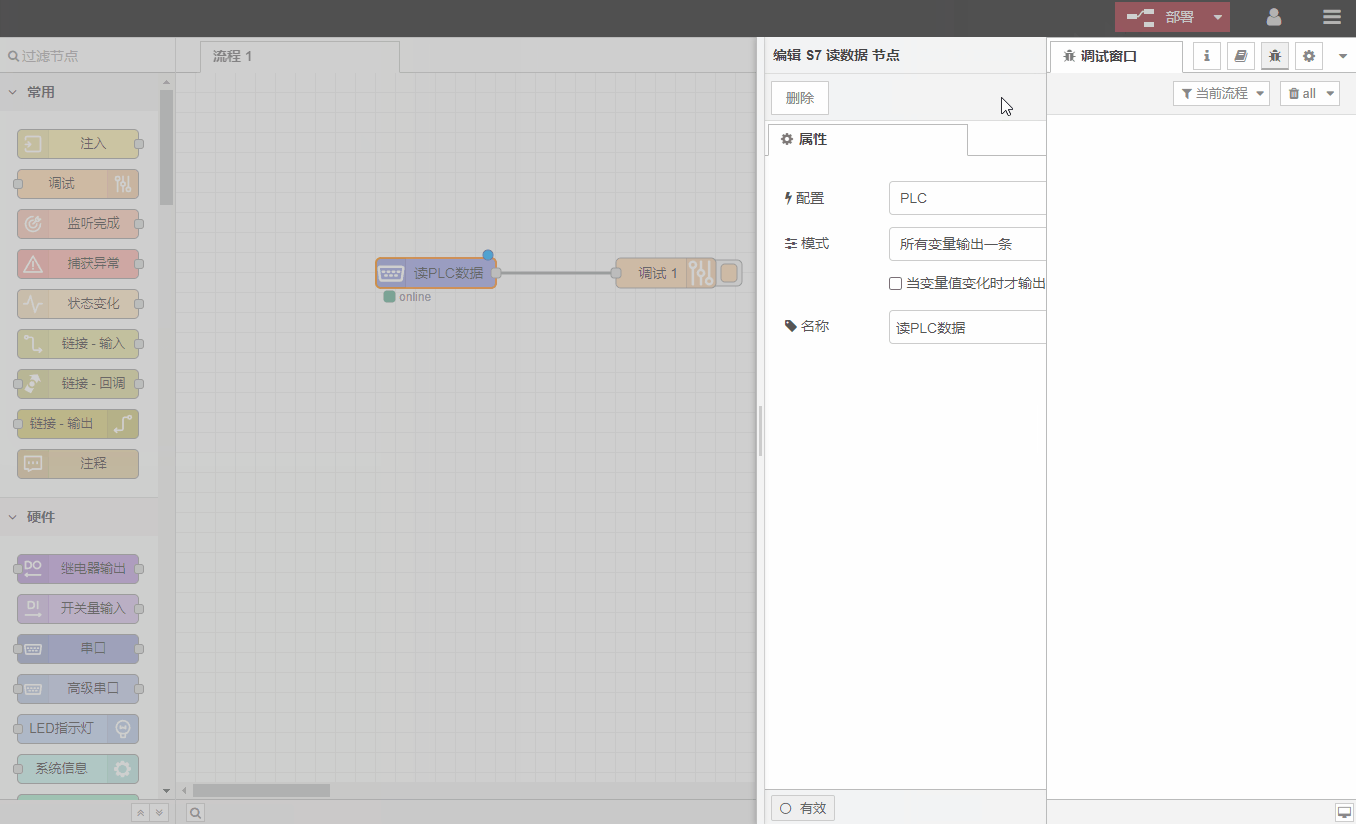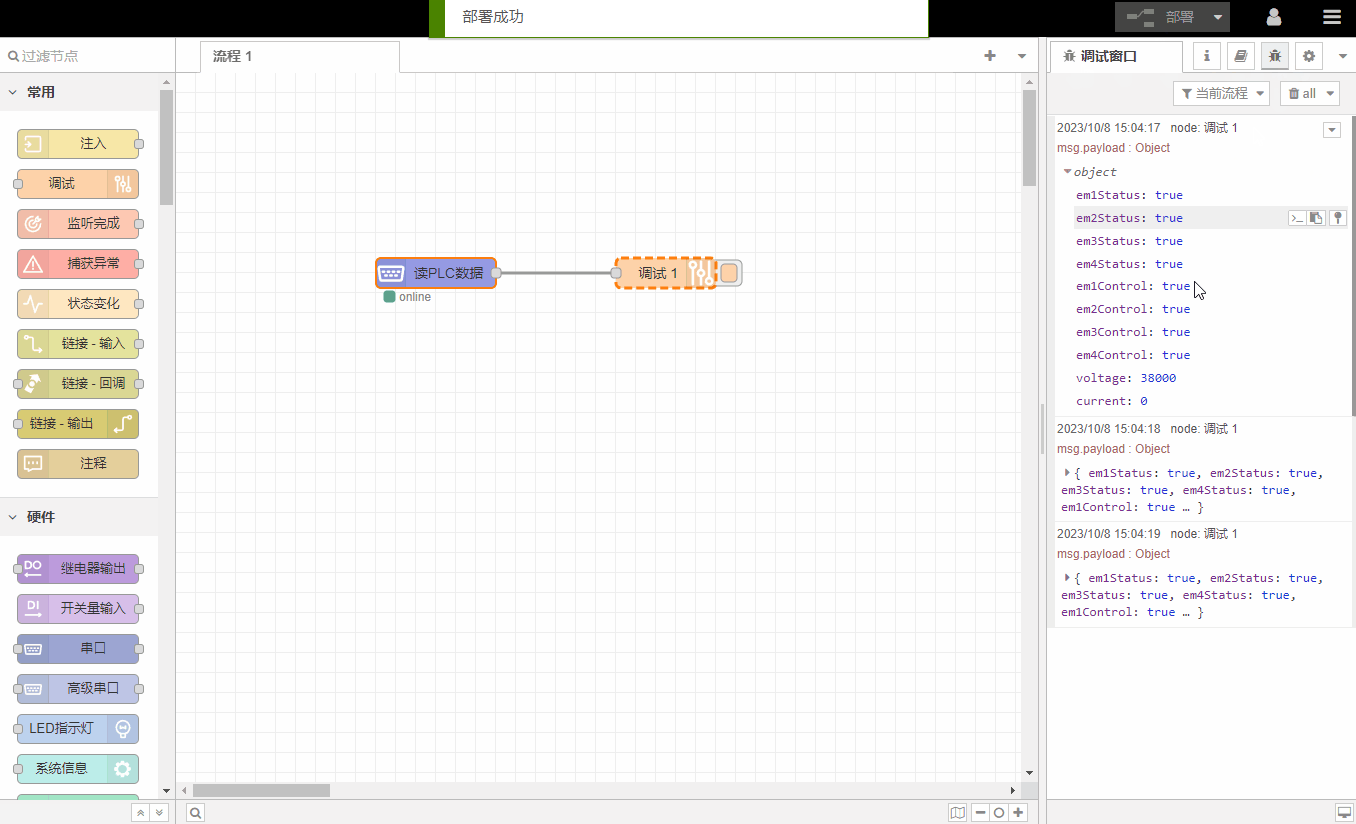
Double-click
S7读数据节点and fill in the corresponding setting parameters according to the requirements overview, as shown in the following figure:
IP: PLC IP port: 102 (S7 protocol communication default port 102) Mode: TASP (S7-200 Smart selects TASP, other models select Rack/Slot) Local TSAP: 1002 (fixed value) Remote TSAP: 0301 (fixed value) ) Collection period: 1000ms (default 1000ms, customizable) Timeout period: 2000ms (default 2000ms, customizable) Data point configuration (the corresponding relationship can be found according to the help document) V0.0-->DB1,X0.0V0.1 -->DB1,X0.1V0.2-->DB1,X0.2V0.3-->DB1,X0.3V0.4-->DB1,X0.4V0.5-->DB1,X0.5V0.6 -->DB1, X0.6V0.7-->DB1,
If the settings are correct, there will be a log print in the debugging window, showing the content of the read data.

-
Sometimes there are many PLC data points, and it is cumbersome to manually enter them one by one. Nodes support the import and export of data points:
2. Data formatting
According to the guidance in step 2, you can see the PLC data read in the debugging window as follows:

Because the application platform has stipulated that data must be reported in JSON format. Next, use 函数节点Javascript code to format the data. The code is as follows:
let jsonArray = []jsonArray.push({ "flag": "em1Status", "switcher": msg.payload.em1Status == true ? 1 : 0 })jsonArray.push({ "flag": "em2Status", " switcher": msg.payload.em2Status == true ? 1 : 0 })jsonArray.push({ "flag": "em3Status", "switcher": msg.payload.em3Status == true ? 1 : 0 })jsonArray. push({ "flag": "em4Status", "switcher": msg.payload.em4Status == true ? 1 : 0 })jsonArray.push({ "flag": "em1Control", "switcher": msg.payload. em1Control == true ? 1 : 0 })jsonArray.push({ "flag": "em2Control", "switcher": msg.payload.em2Control == true ? 1 : 0 })jsonArray.push({ "flag": "em3Control", "switcher": msg.payload.em3Control == true ? 1 : 0 })jsonArray.push({ "flag": "em4Control", "switcher": msg.payload.em4Control == true ? 1 : 0 })jsonArray.push({ "flag": "voltage", "value": msg.payload.voltage / 100 })/*two decimal places*/jsonArray.push({ "flag": "current", " value": msg.payload.current / 100 })/*two decimal places*/let data = {}data.sensorDatas = jsonArraymsg.payload = JSON.stringify(data)return msg
Copy the above code and paste it into the function node. You can see the effect after deployment:

It can be seen that the read PLC data has been converted into the final JSON format according to the requirements, and the data has been calculated to a certain extent (two decimal places).This is just the tip of the iceberg of function nodes. Because it supports Javascript language programming, almost any function you can think of can be implemented here.

3. Report data through MQTT
Drag in an MQTT发布节点, configure it according to the prompts, fill in the MQTT connection related information and the MQTT publishing topic (see the requirements overview for details), and you can implement data reporting. It can be seen that after the data is reported successfully, the application platform displays green to indicate that the device is online and the data is normal:

At this point, data reporting has been completed and can be achieved in a few simple steps: collect PLC data and report it in a custom JSON format.
4. Receive data via MQTT
Drag in an MQTT订阅节点. Note: MQTT发布节点et MQTT订阅节点can share an MQTT connection. If the same connection is used but a different topic, drag in the node and select the configured connection.If you choose to add a new mqtt-broker node, it means creating a new MQTT connection.

Select a debugging node and click the control button on the platform. You can see the issued instructions in the debugging window:

5.Data analysis
According to the help document of the S7写数据node, you can know that in order to write data to the PLC, the data that needs to be passed carries two parameters, as follows:

Therefore, when parsing data, the data sent by the application platform needs to be converted into a message carrying two variables, payload et variable , and passed to S7写数据节点. The code of the function node is as follows:
let cmdDate = msg.payloadmsg.variable = cmdDate.sensorDatas[0].flagmsg.payload = cmdDate.sensorDatas[0].switcher == 1 ? true : falsereturn msg
Copy the above code, paste it into the function node, and set the debug node to output the original message. You can see the printed content as follows:

You can see that the data has been converted to the format required by the S7 write data node.

6.Write to PLC
Drag an S7写数据node, connect 函数计算node, operate the switch on the application platform, and see the demonstration effect:

Résumer
This chapter introduces a relatively complex process, aiming to describe the capabilities of the gateway. Therefore, it does not optimize the security, stability, flexibility, etc. of the program. By understanding this process, I believe you are already familiar with the visual programming of the gateway. Next, learn the function usage of each node in depth. Mastering them will provide you with more choices and possibilities for making more complex processes!
Source code
Tous les processus prennent en charge l'importation et l'exportation au format json, ce qui facilite le partage des processus terminés avec d'autres personnes.The process json file of this chapter is as follows. After copying, select import and paste in the upper right corner of the menu bar. The same goes for exporting.
[{"id":"c8d138cd30e452fc","type":"s7 in","z":"2ff624305b8cb30b","endpoint":"374f5d9e3d2741c0","mode":"all","variable":"", "diff":false,"name":"Read PLC data","x":180,"y":180,"wires":[["03f0b9014af25c1d"]]},{"id":"4abb25e7e75b3447", "type":"mqtt out","z":"2ff624305b8cb30b","name":"Release data","topic":"820000003058164F","qos":"0","retain":"false", "respTopic":"","contentType":"","userProps":"","correl":"","expiry":"","broker":"8d85be060cbc6545","x":520," y":180,"wires":[]},{"id":"63f2816a781192d5","type":"mqtt in","z":"2ff624305b8cb30b","name":"Subscription data","topic ":"820000003058164F/ ","qos":"0","datatype":"auto-detect","broker":"8d85be060cbc6545","nl":false,"rap":true,"rh":0 ,"inputs":0,"x":180,"y":260,"wires":[["1b6776e208355720"]]},{"id":"03f0b9014af25c1d","type":"function"," z":"2ff624305b8cb30b","name":"Data Formatting","func":"let jsonArray = []nnjsonArray.push({ "flag"": ""em1Status""