Explanation of serial communication and parallel communication
Serial communication: data bits are sent one data bit after another, and the data bits represent 0 or 1
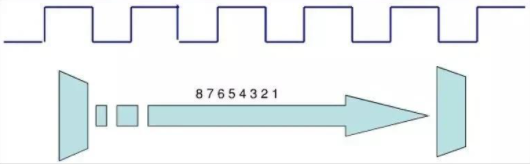
Parallel communication: sending 8 data bits at a time, which is one byte,
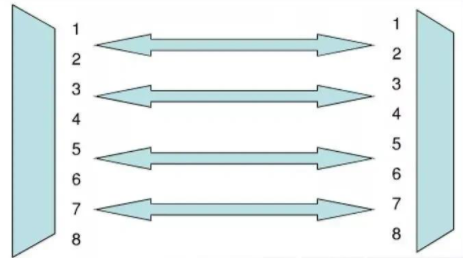
Comparison between serial communication and parallel communication
| serial communication | Parallel communication | |
| Communication distance | Far | close |
| Anti-interference ability | high | Low |
| transfer speed | slow | quick |
| cost | Low | high |
Basic terminology of serial communication
Serial communication method
Code ASCII
Baud rate, parity bit, data bit, stop bit
Communication synchrone et communication asynchrone
DTE and DCE
RS-232
RS-485
RS-422
Serial communication method
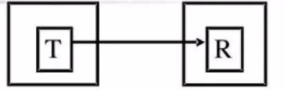
simplex mode
half duplex mode
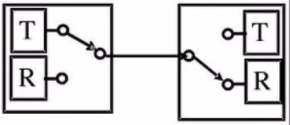
Full duplex mode
The difference between serial and parallel is as follows:
1. The data transmission methods are different: the serial port transmission method is that the data is arranged in a line and sent out and received one by one, and the parallel port transmits 8-bit data and is sent out at one time.
2. The pins are different: there are fewer serial port pins and more parallel port pins.
3. Different uses: The serial port is now only used as a control interface, while the parallel port is mostly used as an interface for printers, scanners, etc.
4. Parallel data transmission uses the computer’s word length, usually 8 bits, 16 bits, and 32 bits as the transmission unit, and transmits one word length of data at a time. It is suitable for short-range information exchange between external devices and the CPU. At the same frequency, the efficiency of parallel port transmission is several times that of the serial port.
5. Serial transmission, or serial communication, refers to using a data line to transmit data bit by bit, and each bit of data occupies a fixed length of time. It only requires a few lines to exchange information between systems, and is especially suitable for long-distance communication between computers and computers and peripheral devices.
The above is the relevant introduction to ” serial communication and parallel communication “.