How to pin gateway
1. Windows operating system, press Windows key R, then enter cmd in the input box
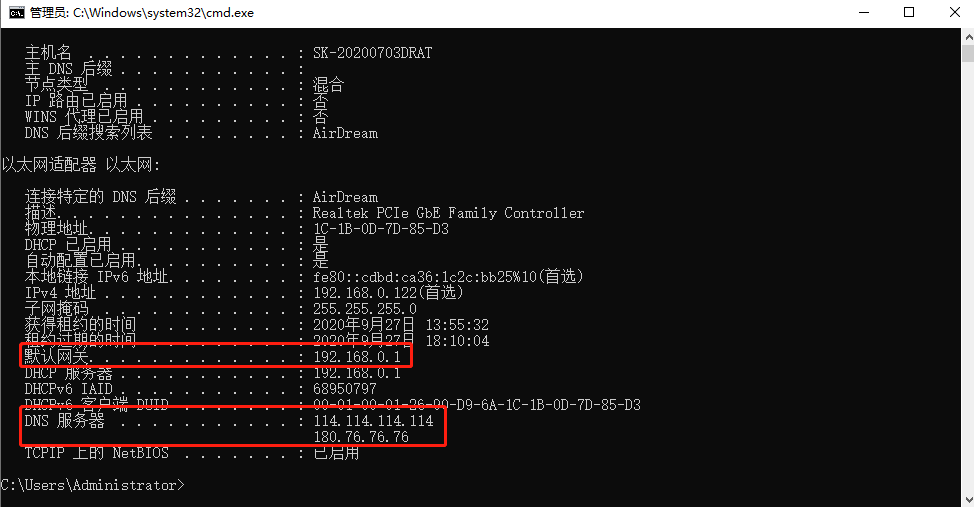
2. Enter ipconfig/all and press Enter to find the default gateway and DNS server.
3. Then we ping the two gateways respectively. The first is the default gateway. You should enter ping 192.69.69.1 -t and press Enter. -t means to keep pinging. After about a few minutes, hold down Ctrl c on the keyboard to terminate it and continue pinging.

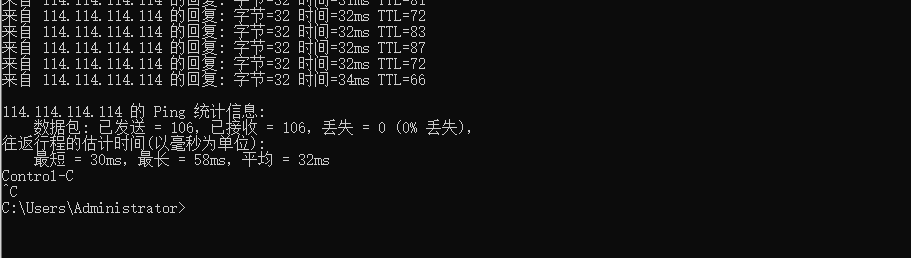
4. Let’s take a look at the status of the network connection. There are two main things to look at. One is to see if there is packet loss, and the other is to see if there is any delay. The picture loss rate is 0, but there is some delay, but it is not a big problem for home use and is a normal phenomenon. If you want a more accurate test, you need to PING a large package or take a longer time.
5. After pinging the router’s gateway, we then ping 114.114.114 -t to the DNS server gateway.
6. The first default gateway of ping 192.168.0.1 is the gateway between the computer and the router. If the ping is successful as shown above, it means there is no problem.
Then ping the second DNS server gateway 114.114.114.114, which is the gateway between the router and the operator.
If the first ping doesn’t hurt and shows that the request has timed out, it means there is a problem between your computer and the router.
If the second ping fails and the request times out, it means there is a problem between your router and your operator.
Analysis of reasons why gateway ping fails
There are many reasons why the gateway cannot ping. This can directly reflect the complexity of the network problem. Sometimes there may be a situation where ping cannot work but you can access the Internet. But most of the time, as long as ping cannot work on the network, there is a problem. The following reason analysis is integrated through some reasons collected on the Internet.
(1) Multi-route load balancing scenarios. For example, when pinging the remote destination host, successful replies and timed outs appear alternately. It turns out that there are two routes to the destination network segment on the gateway router. The weights of the two routes are equal, but there is a problem with one route.
(2) Because the delay between devices in the network is too large, ICM Echo messages cannot be received within the default time (2 seconds). There are several reasons for the delay, such as lines (the satellite network delay is 540 milliseconds for up and down satellites), Hong Kong server rental router processing delay, or unreasonable routing design causing roundabout paths. Use extended ping and increase the timedout time. If the ping succeeds, the problem is that the routing delay is too large.
(3) When NAT is introduced, one-way ping will occur. NAT can hide the internal address. When pinging from the inside to the outside, the ping can be successful because the mapping relationship in the NAT table exists. When pinging the internal host from the outside, there is no way to find the NAT entry of the border router.
(4) IP address allocation is discontinuous. Problems with address planning are like laying mines in the network. Overlapping addresses or discontinuous mask divisions may cause problems during ping. For example, in an extreme case, two hosts A and B are connected through multiple hops. A can ping B’s gateway, and B’s gateway is set correctly, but A and B cannot ping. After investigation, it was found that there is a second address on B’s network card, and this address overlaps with the network segment where A is located.
(5) Too impatient. That is, trying to ping the gateway as soon as the network cable is plugged into the switch, ignoring the spanning tree convergence time. Of course, newer switches support rapid spanning tree, or some administrators simply turn off the spanning tree protocol on the user port (access port), and the problem is solved.
(6) Some router ports do not allow users to Ping.
(7) Access control. No matter how many hops are spanned in the middle, as long as there are nodes (including end nodes) filtering ICMP, it is normal for Ping to fail. The most common is the behavior of firewalls.
(8) Extended Ping to specify the source address. Log in to the router and ping the remote host. When the ICMP echorequest is sent from the serial WAN interface, the router will specify a certain IP address as the source IP. This IP address may not be this interface. The IP or this interface has no IP address at all. A certain downstream router may not have a route to this IP network segment, causing the ping to fail. You can use extended Ping to specify the source IP address.