Foreword:
Describes the development status of wireless communication technology for smart gas meters, analyzes the characteristics of NB-IoT communication technology applied in smart gas meters, and points out the problems existing in smart gas meters using NB-IoT communication technology (lack of necessary transaction authentication mechanisms, lack of Gas data professional processing capabilities and technical maturity are insufficient). Smart gas meters solve the above problems through built-in gateways. Specify the structure of the smart gas meter with built-in gateway and the structure and function of the gateway. The built-in gateway has information security protection functions, can perform communication authentication and transaction authentication, has professional gas data processing capabilities, and can ensure the synchronization of smart gas meter application upgrades with telecom operator network upgrades. Discuss the information interaction process between smart gas meters and gas company servers.
Current status of wireless communication technology for smart gas meters
The communication technologies that can be used by smart gas meters include wired communication technology and wireless communication technology. With the advancement of wireless communication technology, more and more smart gas meters choose to use wireless communication technology, overcoming the problems of high line laying costs, difficult equipment maintenance, and poor network scalability of wired communication technology. Wireless communication technologies currently used in smart gas meters include Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN), Wireless Wide Area Networks (WWAN) and Low Power Wide Area Network, LPWAN) Category 3, the classification of wireless communication technology is shown in Figure 1.
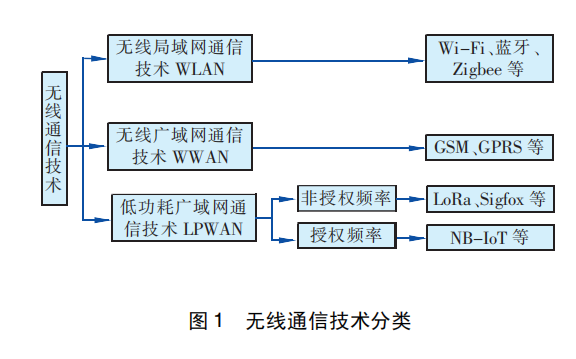
Under the general trend of the Internet of Everything, traditional wireless communication technology can no longer meet the needs of the Internet of Everything (wide coverage, low power consumption, large connections, etc.), and it is urgent to develop a new Internet of Things communication technology to achieve
Everything is now interconnected. Under this demand, Narrow Band-Internet of Things (NB-IoT) communication technology came into being. The emergence of NB-IoT communication technology originated from the joint efforts of public telecom operators (hereinafter referred to as telecom operators), communication equipment manufacturers, and chip designers. It is a brand-new narrowband Internet of Things technology based on cellular networks. It is a 3GPP organization The defined international standard can be directly deployed on existing telecommunications networks [1]. 2 NB – Characteristics of IoT applications in smart gas meters
① Communication network structure using NB-IoT technology
The smart gas meter NB-IoT communication network structure is shown in Figure 2.The smart gas meter can upload sensing information from the smart gas meter through the telecom operator’s sensor network communication platform, and at the same time receive gas company information.
The control information issued by the company server. NB – IoT base station can realize the management of wireless resources (such as network access authentication of terminal devices, verify whether the device has the right to access the network and system, prevent illegal devices from accessing the network and occupying network resources) and encrypt the passing data stream, And the encrypted data is processed through the gateway and uploaded.
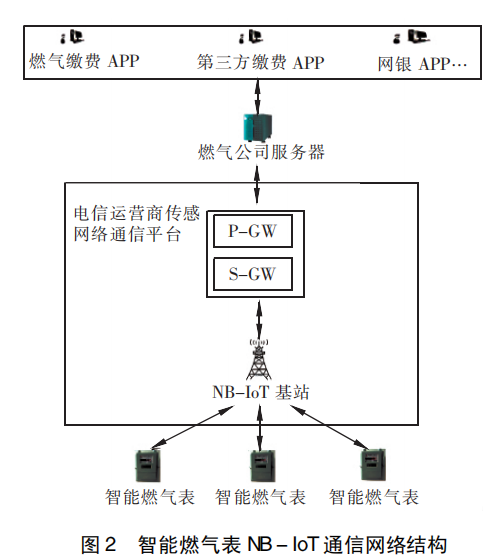
The gateways provided by telecom operators include Serving Gateway (S-GW) and Packet Data Gateway (PDN Gateway, P-GW). S-GW is responsible for managing smart gas meter communications, including the establishment and release of connections, enabling service quality control, and storing smart gas meter terminal context information (including smart gas meter terminal logo information, communication network element addresses, etc.). The P-GW gateway is responsible for managing the connection of the external data network, realizing the network access authentication of the external data network, and realizing the connection between the telecom operator’s sensor network communication platform and the gas company’s server.
The gas company server classifies and calculates the received meter-end sensing data, and stores the processed data information locally for easy call at any time. The gas company server analyzes the received meter data to perceive the status of the meter, and then manages the meter. At the same time, the gas company server can receive query information and control information sent by gas users to realize services for gas users and control the meter according to the wishes of gas users.
② Problems with NB-IoT application in smart gas meters
Compared with smart gas meter communication networks using other wireless communication technologies, a significant feature of the smart gas meter communication network using NB-IoT communication technology is that the communication between the smart gas meter and the operator base station does not require independent networking, that is, smart gas meter communication. The gas meter can communicate directly with the telecom operator’s sensor network communication platform, ensuring communication security during information transmission, but there are the following problems.
a. Lack of necessary transaction authentication mechanism. NB-IoT communication technology is a paid and reliable communication technology in controlled frequency bands. Any real-name authenticated communication node in the network covered by its base station has the right to communicate legally, and its legal identity can be recognized through the network anytime and anywhere to obtain communication rights. , ensure communication security. However, it lacks business security assurance capabilities and cannot identify the legality of gas transactions between the gas company (gas company server) and gas user equipment (smart gas meter). As a result, the gas user or gas company’s legal contract cannot be performed normally when problems arise. , affecting the normal development of the gas company’s business. For example, after an attacker obtains the communication rights of the NB-IoT base station and sends illegal data to the smart gas meter by simulating the gas company server, the gateway in the telecom operator’s sensor network communication platform can only authenticate the communication and cannot know the communication object. Whether it is legal or not means that transaction authentication cannot be achieved, so that illegal data can directly reach the smart gas meter, posing a threat to the data security of the smart gas meter and the safety of gas use. Therefore, in addition to identifying communication rights, the transaction rights of both gas companies and gas users should also be identified.
b. Lack of professional gas data processing capabilities. The gateway in the telecom operator’s sensor network communication platform is essentially a network management platform, which can manage the establishment and release of the network and ensure the security of gas data during transmission. However, the gateway of the telecom operator’s sensor network communication platform does not have the function specifically for processing and analyzing gas data. For reasons of commercial confidentiality, the gas company does not want third parties to participate in the processing and analysis of gas data. This has led to the telecom operator’s The sensor network communication platform transmits all transmitted data to the meter end for processing. This puts forward higher requirements for the meter end and requires a professional gas data processing module built into the meter end.
c. The technology is not mature enough. In practical applications, NB-IoT communication modules (such as communication protocols, etc.) need to be continuously upgraded and optimized, which will have an impact on enterprise products and products already in service. At the same time, telecom operators’ network upgrades and NB-IoT module upgrades cannot do this. Completely synchronized, it is easy for telecom operators to upgrade their networks and fail to upgrade their meter-side communication modules in a timely manner, which affects the gas company’s normal business operations and cannot provide efficient and high-quality services to gas users.
3Smart gas meter with built-in gateway
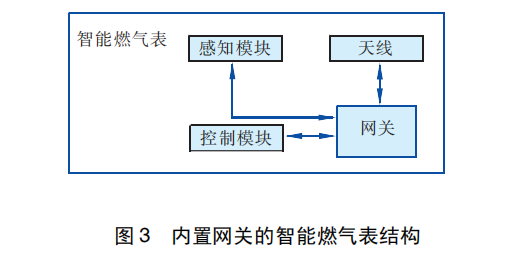
① The smart gas meter structure with built-in gateway NB-IoT communication technology is suitable for the communication of smart gas meters. It can well solve the problem of smart gas “connection” and has incomparable advantages compared with traditional wireless communication technology. But at the same time, we must realize that NB-IoT communication technology lacks the management function of the meter, and in practical applications it needs to be combined with a smart gas meter with a built-in gateway. The structure of the smart gas meter with built-in gateway is shown in Figure 3. The gateway of the smart gas meter is connected to the sensing module and control module, and is connected to an external antenna.The gateway can process the sensing information transmitted from the sensing module, including flow
quantity information, temperature and pressure information, clock information, etc.; at the same time, it can receive control information sent by the gas company server through the antenna, such as valve closing information, locking information, recharge information, etc. The gateway processes these information and transmits them to the control module. The control module controls the working status of the smart gas meter.
② Gateway structure and functions The gateway structure is shown in Figure 4.
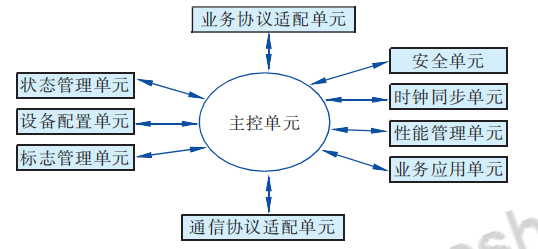
The functions of each unit are as follows.
a. Main control unit: used to receive and send request instructions, control instructions and business data, to realize the uploading of table-side sensing information and the reception of remote control information and query information. The main control unit exchanges data with the sensing module, control module and antenna in Figure 3, which are not shown in Figure 4.
b. Equipment configuration unit: used to receive control instructions from the main control unit and upload request instructions to the main control unit to manage the working status of each module of the smart gas meter. c. Communication protocol adaptation unit: used to convert the format of the control instructions and business data information issued by the gas company server into a format that the main control unit can receive, and to convert the format of the request instructions and business data information uploaded by the main control unit into A format that the gas company server can receive.
d. Flag management unit: realizes the unified identification of gateway flags, gas meter base meter flags, control module flags, sensing module flags and network address flags, and realizes functions such as reading and configuring various flags. The flag management unit compares the identified various flags with the NB-IoT base station flag and the gas company server flag received by the gateway in the main control unit, and combines the functions of the security unit to realize communication authentication and transaction authentication.
e.Status management unit: used to transmit request instructions for dispositivo gateway status information and business application status information obtained by the gas company server. It can also actively and regularly send requests to the gas company server.
Transmit gateway device status information instructions and business application status information instructions to realize the gas company server’s perception of the operating status of the smart gas meter.
f. Security unit: The security unit is mainly responsible for explosion-proof safety management and information security management. Explosion-proof safety management is to identify the abnormal gas usage status of smart gas meters and transmit the abnormal information to the main control unit, which determines the preventive measures to be taken to ultimately ensure the safety of gas users. Information security management is to identify and filter the external information received by the smart gas meter to prevent illegal control information from being executed incorrectly. At the same time, it encrypts the uploaded meter-side sensing information to prevent information from being stolen.
g.Clock synchronization unit: The clock synchronization unit communicates with the main control unit and is used to receive clock synchronization instructions issued by the main control unit and actively upload request synchronization instructions to the main control unit to ensure smart gas meters.
The meter clock is synchronized with the gas company’s server clock to improve communication efficiency and ensure metering fairness. h. Performance management unit: used to transmit automatic detection and maintenance control instructions to the main control unit, and at the same time transmit request instructions initiated by the gas company server to obtain gateway performance data and collect performance parameters of the main control unit.
i.Business protocol adaptation unit: Convert the information format of the control instructions and business data information issued by the main control unit into a format that can be received by each management unit, and convert the information sent by each management unit in the gateway
The format of the request instruction and business data information is converted into a format that the main control unit can receive.
j. Business application unit: The business application unit communicates with the main control unit and is used to manage the applications inside the gateway, including application loading, installation, monitoring, uninstallation, activation, deactivation, upgrade, etc., to ensure the normal progress of communication and prevent errors. The telecom operator’s network was upgraded and the table-side application upgrade was lagging behind, causing normal communication to fail.
③Information exchange process
The interactive information between the smart gas meter and the gas company server includes uplink messages and downlink messages. The uplink message refers to the information data uploaded by the smart gas meter to the gas company server, and the downlink message refers to the information data sent by the gas company server to the smart gas meter. information data. The communication between the smart gas meter and the gas company server is divided into active communication and passive communication. Active communication means that the smart gas meter uploads information to the gas company server in specific situations (such as potential safety hazards at the meter end, etc.) or at regular intervals. Passive communication It means that after the gas company server sends information to the smart gas meter, the smart gas meter uploads the information to the gas company. The information interaction process of the built-in gateway smart gas meter is shown in Figure 5.
a. The gas company server sends query, setting, control and other information to the smart gas meter, which can be transmitted to the smart gas meter through the telecom operator’s sensor network communication platform. This information is called downlink message information, and the downlink message information is passed through twice Encryption, the smart gas meter gateway finally parses and stores the downstream message information, completes the transaction authentication by comparing it with the sensing module and control module flags, forms a control instruction, and sends it to the sensing module and control module to complete the intelligent Query, configuration and control of gas meters.
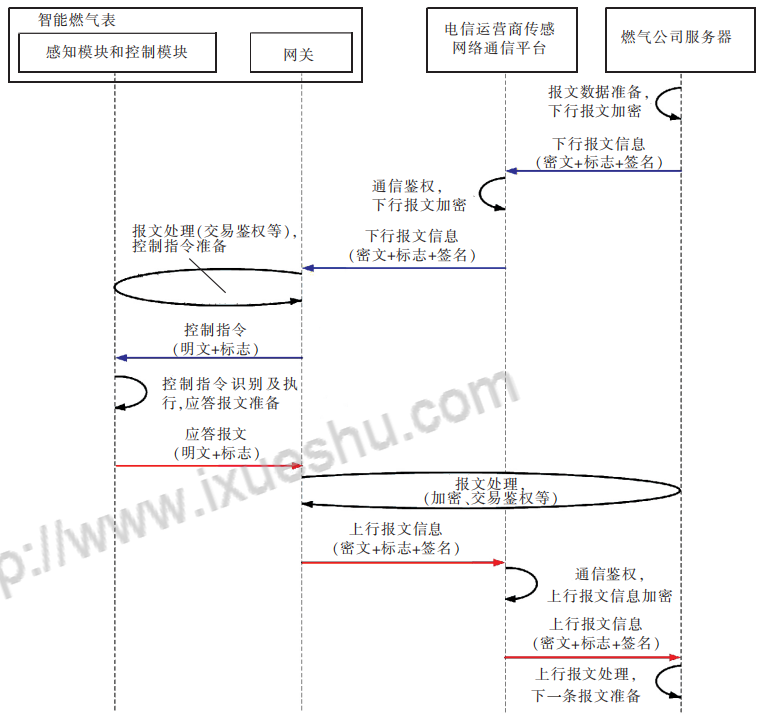
Figure 5 Information interaction process of built-in gateway smart gas meter
b. After the sensing module and control module execute the command, a response message will be formed, that is, the feedback information is transmitted to the gateway, and the transaction authentication is completed by comparing it with the gas company’s server logo, IP address, etc., and then encrypted and stored to form The uplink message information is re-encrypted by the telecom operator’s sensor network communication platform and then transmitted to the gas company server. The gas company server parses, stores and processes the uplink message information to prepare for the next message.
The message information contains specific information such as signs and signatures, which are used to complete communication authentication and transaction authentication. The message information during transmission exists in the form of ciphertext to ensure the security of communication information.
Disclaimer: This article is reproduced online. If it infringes upon your interests, please contact us to delete it!