Introduction to Edge Computing Architecture
Edge computing architecture is a new model for providing storage and a large number of computational attributes around the system. This approach brings storage and computation closer to the device, improving response time and reducing bandwidth. Edge computing involves all types of computation at the edge of the network outside the cloud. Edge time deals with real-time dynamics generated by sensors and real-time applications. The presence of a large number of IoT devices pushes bandwidth requirements to extreme levels, resulting in latency. Edge computing brings services closer to the edge and enhances service delivery.
1. Data sources/devices
Data sources in edge computing environment can be applications, sensors, devices and any data capturing devices to capture data. Such devices generate data from different sources. The databases vary depending on the function and location. Various edge devices capture data and communicate through IoT protocols to send data to the gateway edge. The protocols used for data transmission can be Ethernet, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, NFC, ZigBee, etc. In simple words, every data generating device will be considered as an edge device.
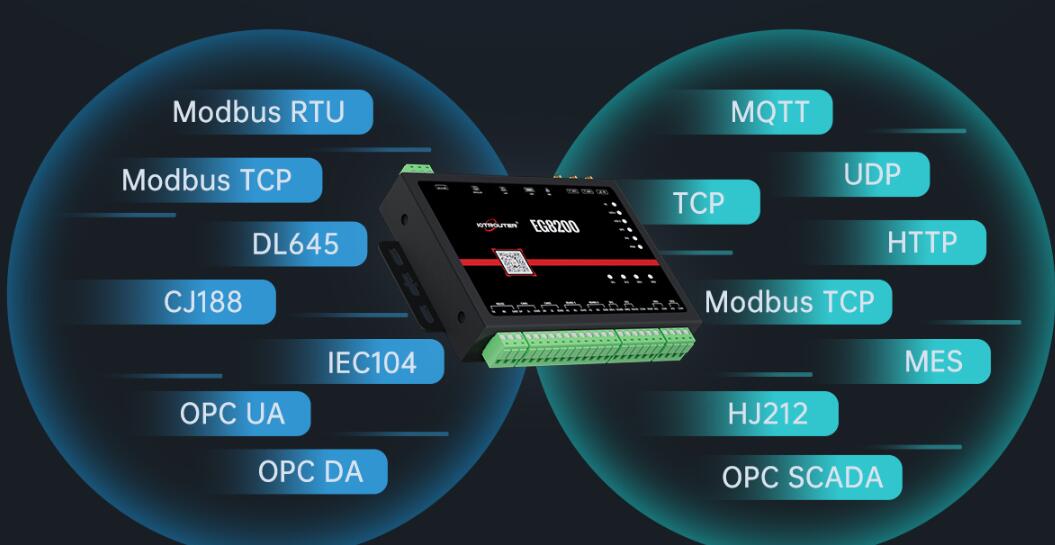
2. Edge Gateway
The edge gateway acts as a node between the edge device and the core network. The core network consists of fully functional devices with adequate data pre-processing. Edge gateways are used to provide interface for wired and radio based transmissions.
3.The various standards used are
Z-Wave (Z-Wave) : Z-Wave is used for 30 meter point-to-point communication and is specialized for small transmission applications such as home appliance control applications. Z-Wave operates in the middle of the ISM band (about 900 MHz) and allows 40 kbps transmission speed. Z-wave is known as the best choice for communication of home appliances.
LTE-A (Long Term Evolution-Advanced): the communication protocol consists of a set of various protocols used for communication and belongs to the IoT-based machine signaling and architecture. It outperforms other cellular solutions in terms of cost of service and scalability.
EPC Global: Electronic device code is used to identify items in supply chain management and only the identification number is stored on the RFID tag. The architecture uses RFID technology and easy to use RFID identification and readers for information sharing. This architecture is recognized as a promising technology for the future of the Internet of Things because of its openness and scalability.
Bluetooth Low Power: Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) or Smart Bluetooth uses radio signals over short distances and with minimal power requirements. It operates over about ten times the range of classic Bluetooth technology. It has fewer delay factors compared to classic Bluetooth technology 15 times.
Protocols used
1. CoAP
CoAP was established by the IETF Constrained RESTful Environments (CoRE) In edge devices and applications. the working group established an application layer protocol. the CoAP proposes a situation-based transport based on the HTTP in functionality. (REST) transport protocol. REST It is a cachable connection protocol that relies on a stateless client-server architecture. It represents the right way for clients and servers to exchange data on top of HTTP. It is used in mobile device-based social networking applications and uses HTTP methods (get, post, put, and delete) to reduce complexity.
2. MQTT
MQTT is used to establish connections between embedded devices, service networks and middleware. Connection operations based on routing mechanisms MQTT turns out to be an excellent connectivity protocol for IoT and M2M.MQTT is built on top of the TCP protocol for devices with low resource availability, unreliable or low bandwidth links.MQTT consists of only three parts: subscriber, uploader and proxy.
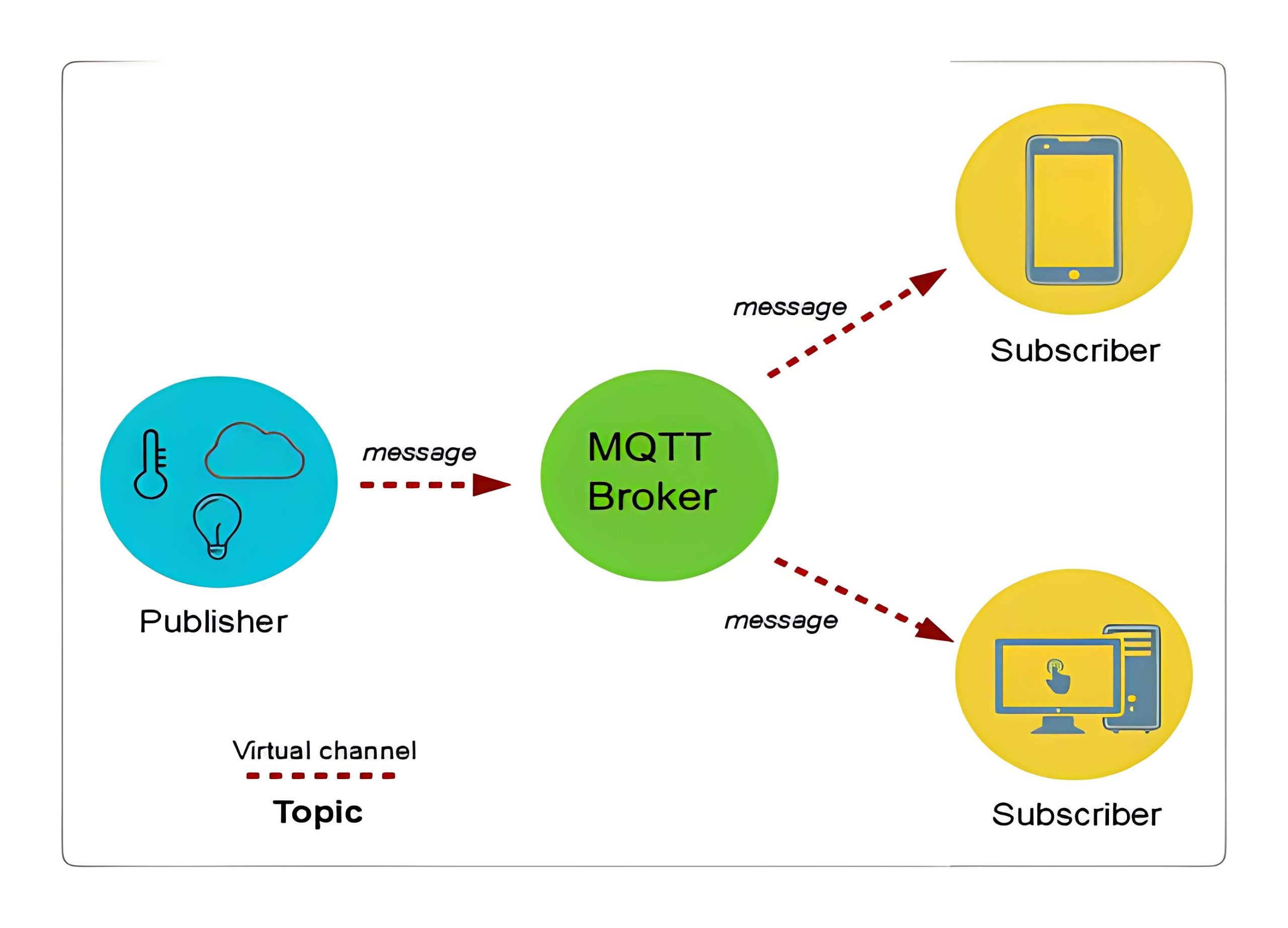
3. AMQP
AMQP is an open standard application layer protocol dedicated to news-oriented environments. It ensures that the original language provides reliable communication through messaging. including at most one. at least one. and just right. the TCP reliable protocol for message exchange.
Conclusione
Edge computing is designed to enable instant applications to work efficiently and deliver responses within a specified time frame. The system architecture focuses on reducing bandwidth usage and minimizing latency. The architecture can include cloud-based effects, as in many cases, and in some cases, cloud features are not included in the edge architecture model.
The fabric has a modest interface to cloud data centers, enabling permanent cloud-based data storage and other services. The edge fabric is flexible enough to add devices from different heterogeneous environments, providing closer proximity to devices