The latest research data from market research company Counterpoint Research shows that global IoT cellular connections are expected to exceed the 5 billion mark by 2025, and China will continue to lead the world with nearly two-thirds of the number of connections.
Global IoT cellular connections grew 72% in the first half of 2018, according to Counterpoint, which the research firm said was “significant growth” compared to the same period last year.
China is currently the world’s largest cellular IoT market, with China’s three major telecom operators – China Mobile, China Unicom and China Telecom – accounting for 70% of global IoT connections. In 2025, 66% of global IoT connections are expected to come from the IoT networks of these three operators.
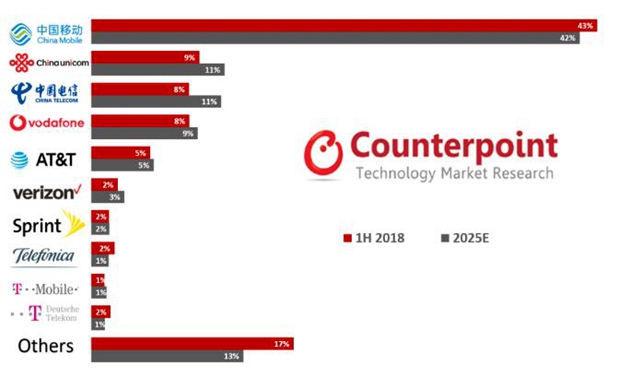

Comparison of global cellular IoT connectivity market share in the first half of 2018 and 2025
Counterpoint research analyst Satyajit Sinha said: “Emerging markets such as India, Brazil and Africa can provide huge scale, but compared with China, they may be lagging followers in terms of IoT deployment.”
“However, there is still a huge opportunity for growth in cellular IoT connectivity in emerging markets, which may be driven by operators such as Reliance Jio in India, but more specifically by multinational operators such as Telefónica, MTN and Vodafone .” Sinha pointed out.
Sinha said that smart manufacturing, smart utilities and smart mobile applications (such as automobiles and asset tracking) will become the main growth drivers of IoT deployment in the next 5 to 7 years.
NB-IoT will become the dominant connectivity technology
On the technology side, Counterpoint’s report predicts that NB-IoT will account for 45% of global IoT cellular connections by 2025, thanks to the diversity of application opportunities and faster adoption across the ecosystem.
By then, 2G IoT connections will account for less than 1% of global IoT cellular connections. Because they are increasingly being replaced by NB-IoT.
3G IoT connectivity will also face the same fate as 2G. However, 3G will be phased out faster than 2G.
4G LTE IoT connectivity (high bandwidth and low latency) will grow at a faster rate until 2022 due to the global deployment of LTE-A and LTE-A Pro.
At the same time, the growing popularity of NB-IoT and unlicensed LPWA will also squeeze the opportunity and share of LTE-M, which will emerge by 2022 and account for about 6% of global IoT cellular connections by 2025 .
“Most IoT connections are still on 2G/2.5G networks,” said Peter Richardson, director of research at Counterpoint. “However, the shift to 4G LTE and cellular-LPWAN has already begun, and we expect the shift to these new technologies to continue in the second half of 2018 and into 2019.”
While cellular-LPWAN offers many advantages over unlicensed LPWA solutions, Richardson added that in many use cases, unlicensed technology offers both cost and functionality.
“In the short to medium term, we expect licensed and unlicensed LPWA technologies to coexist or even be used in combination,” he said.
Counterpoint said that as the industry smoothly transitions to 5G starting in 2020, 4G LTE IoT connections will account for more than one-third of global IoT cellular connections in 2025.
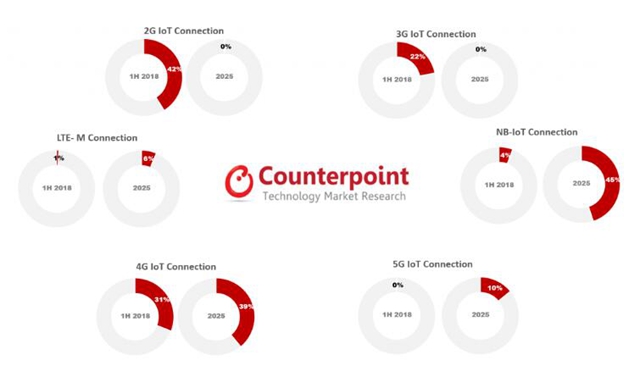

Comparison of global IoT cellular connectivity technology market share in the first half of 2018 and 2025
“5G will be critical to some industries, such as the automotive industry, especially in V2V and V2X. The adoption of 5G cellular technology will depend on the availability and cost of modems from companies such as Qualcomm and Huawei, as well as the coverage of the network. We expect 5G will account for approximately 10% of global IoT cellular connections in 2025,” Richardson concluded.