Wireless communication modules enable various types of terminal equipment to have the ability to transmit networked information. As the underlying hardware, they are irreplaceable and are a key link in connecting the perception layer and network layer of the Internet of Things.
Based on the characteristics of electromagnetic signals propagating freely in space, people can transmit sound, text, data, images and other information over long distances without cables, and receive and send electromagnetic signals and convert data information through mobile terminals such as mobile phones. In the same way, in the Internet of Things era, the connection between things also requires a similar device to send and receive signals. This is a wireless communication module, a collection of chips and peripheral integrated circuits.
The wireless communication module is the information entrance for various smart terminals to access the Internet of Things, enabling Internet of Things terminal equipment to have the ability to transmit networked information. All device data generated by the IoT perception layer are aggregated to the network layer through the wireless communication module, and then the devices are remotely managed and controlled through the cloud management platform. At the same time, through data analysis, management efficiency is improved.
Therefore, there is a one-to-one correspondence between the wireless communication module and the IoT terminal.
The two are closely linked and are the basic links of the Internet of Things such as agriculture, industry, urban management, telemedicine, smart homes, and smart transportation.
The module itself is a very broad concept. For example, a software module refers to a collection of program statements that can be individually named and independently complete a certain function (that is, a collection of program codes and data structures). A hardware module refers to a module composed of multiple components with basic functions. A system with complete functions can be divided into communication modules, positioning modules, photosensitive modules, etc. according to functions. In the field of Internet of Things, when mentioning modules, most of the time it refers to wireless communication modules.
For wireless communication modules, the upstream products are raw materials such as baseband chips, which are highly standardized. Baseband chips (communication chips) are the core, accounting for about 50% of material costs. Technical barriers are high. The main suppliers include Qualcomm, Intel, MediaTek, RDA, Huawei, etc., with high product concentration and strong corporate voice. Downstream applications are distributed in various vertical market segments, and usually flow from the communications intermediate distribution and consignment links to various industry fields. The module provider purchases upstream materials and is responsible for design and sales, while the production process is outsourced to third-party processing plants.
Wireless communication modules are divided into large particle market and small particle market according to the size of the application market. The large particle market has a large number of IoT modules, a high degree of standardization, and fierce competition. It is suitable for increasing revenue and establishing a brand. It has relatively few R&D personnel, but has strong market development capabilities; the small particle market has a small quantity of IoT modules and is customized. The degree is high and the gross profit margin level is high, but the requirements for suppliers’ R&D investment are relatively high.
For the wireless communications industry, upstream chips and downstream applications cannot be independent of each other. The upstream and downstream manufacturers in the industry chain must assemble the chips and other components together to complete the entire machine assembly before communication can be achieved. In the same way, if a device wants to “call” another device and directly give it a component (for example, embedding a baseband chip into the device), it obviously cannot do anything. It must go through the module manufacturer to transfer the baseband chip, radio frequency, Various components such as memory chips, capacitors, and resistors are integrated together to form a “mobile phone” that can be directly used by the device. The device can then be used to “make calls” directly after inserting a card. This is the first value of the module in the IoT industry chain: hardware integration and software design, integrating multiple communication formats to meet environmental requirements in different application scenarios, greatly simplifying the work of application manufacturers.
Wireless communication module products
| Esterno | Nome/Modello | interfaccia | Caratteristiche |
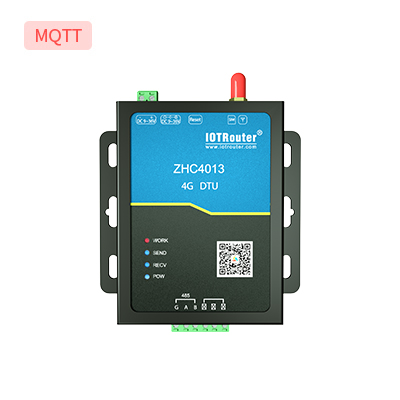 |
4G DTU ZHC4013 |
RS485 |
Supporto del protocollo MQTT Supportare la raccolta attiva dei dati Supporto del protocollo JSON Riavvio/trigger programmato |
 |
4G DTU ZHC401C |
RS485 |
Supporto del protocollo MQTT Supportare la raccolta attiva dei dati Supporto del protocollo JSON Riavvio/trigger programmato |
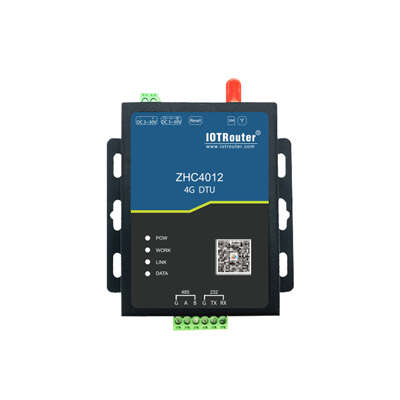 |
4G DTU ZHC4012 |
RS485 |
Supportare la raccolta attiva dei dati Spegnere e ricollegare Doppio watchdog Antisurriscaldamento |
Keywords: 4g industrial dtu