As people’s demand for agricultural products becomes higher and higher, the application scope of the Internet of Things in agriculture is becoming more and more extensive. The foundation of the agricultural Internet of Things is agriculture, and the process is networking. The purpose is to realize digital agriculture and precision agriculture, react on agriculture through data, models, and algorithms, guide agricultural production, and ultimately achieve the “unmanned” development of agriculture.


However, the ideal is very full, but the reality is very skinny. In fact, some agricultural IoT companies appeared in China a few years ago. However, after this year’s development, these agricultural IoT companies have yet to form an industrialized and replicable business model. Although some companies have obtained certain capital returns in the capital market (New Third Board), most companies are still in the exploratory stage.
Investigating the reasons why agricultural Internet of Things companies develop slowly, this article summarizes the following two points:
1. There are various types of agricultural products in China, and one set of equipment is not enough to measure all varieties.
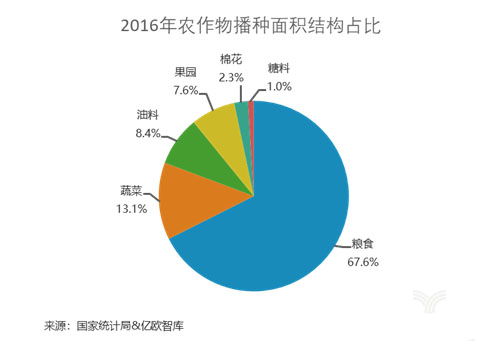

There are various types of agricultural planting, including food crops, cash crops, vegetable crops, etc., and cash crops include cotton, oil crops, fruits, etc. According to statistics from the National Bureau of Statistics, among the sown area of crops in China in 2016, the sown area of grain accounted for 67.6%, followed by vegetables, which accounted for 13.1%. There are many types of crops in China, but due to technical and cost reasons, agricultural IoT companies cannot yet be applied to all crops. At the current stage, they can only be applied to a few major application places such as vegetable gardens, orchards, and tea gardens. The same set of IoT devices is not replicable yet, and at this stage it is often focused on a specific project.
2. The price of downstream agricultural products is low. The use of the Internet of Things increases production costs, but the sales price cannot go up.
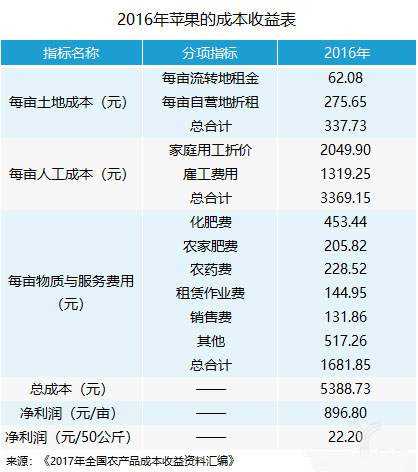

Agricultural IoT devices can be applied to a variety of crops, including vegetables, fruits, etc. Taking apples as an example, the total cost of growing apples per mu in 2016 was 5,388.73 yuan, of which land costs, labor costs, and material service costs were 337.73 yuan, 3369.15 yuan, and 1,681.85 yuan respectively. Labor is the main source of production costs; in terms of materials, Among the service fees, fertilizer is the most important cost. The use of agricultural IoT equipment can reduce problems such as the use of personnel and the waste of fertilizers. However, some tasks that require experience or complexity, such as pruning and bagging, also require manpower. At the same time, a set of IoT equipment (including weather stations, sensors, etc.) and software systems, etc.) also range in price from several thousand to tens of thousands, with an average of at least a few hundred yuan per mu, but the net profit per mu is only a few hundred yuan (take Apple as an example), and it also faces the problem of slow sales. , so the current agricultural IoT equipment is mainly used in large-area growers and growers whose crops have higher economic value. It will take time to apply IoT equipment in large areas.
The use of IoT devices can achieve remote monitoring and solve the abuse problems of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, etc. High prices and immature technology are the main problems currently faced by the industry. But digitalization is the trend of future development. The agricultural Internet of Things relies on digitalization to obtain a large amount of data, achieve precise and efficient production, liberate manpower, and improve the rational utilization and distribution of resources. Although there are still many problems at this stage, the government Units, relevant research scholars, and major agricultural technology companies are vigorously promoting the digital transformation of agriculture.
Agriculture is a sentimental industry. Only through patient and continuous cultivation can we solve the current problems faced by agriculture and ultimately realize the modernization and intelligent development of agriculture.