In the previous article on this site “Short-distance Wireless Communication Networking Technology”, there was a brief introduction to LoRa. The space is limited and it is certainly not possible to explain the LoRa technology in detail, so today we will write a special article about ” lora “Technical Principles ” article. The protagonist of the article is LoRa, which will be used throughout the article.
As mentioned in the previous article, LoRa is one of many LPWAN communication technologies. It is a long-distance wireless transmission technology based on spread spectrum technology. It was first adopted and promoted by the American Semtech company.
LoRa is a physical layer or wireless modulation used to establish long-distance communication links. Many traditional wireless systems use frequency shift keying (FSK) modulation as the physical layer because it is a very efficient modulation that achieves low power consumption. LoRa® is based on linear frequency modulation spread spectrum modulation, which maintains the same low power consumption characteristics as FSK modulation, but significantly increases the communication distance. Linear spread spectrum has been used in military and space communications for decades due to its ability to achieve long communication ranges and robustness to interference, but LoRa® is the first low-cost implementation for commercial use.
1. Lora network architecture and principles
In a mesh network, individual terminal nodes forward information from other nodes to increase the communication distance of the network and the size of the network area. While this increases range, it also increases complexity, reduces network capacity, and reduces battery life as nodes accept and forward information from other nodes that may not be relevant to them. When implementing long-distance connections, the long-distance star architecture makes the most sense to protect battery life.
In a LoRaWAN® network, nodes are not associated with dedicated gateways. In contrast, data transmitted by one node is usually received by multiple gateways. Each gateway forwards packets received from the end node through some backhaul (cellular, Ethernet, etc.) to a cloud-based network server. The intelligence and complexity are placed on the server, which manages the network and filters incoming data for redundancy, performs security checks, schedules confirmations through optimal gateways, and performs adaptive data rates, etc.
2. LoRa wireless technology network composition
The LoRa network is mainly composed of four parts: terminal (can have built-in LoRa module), gateway (or base station), server and cloud. Application data can be transferred in both directions.
LoRa Alliance The LoRa Alliance is an open, non-profit organization led by Semtech in March 2015. Its founding members include French Actility, Chinese AUGTEK and Royal Dutch Telecom kpn. In less than a year, the alliance has developed more than 150 member companies, including many heavyweight manufacturers such as IBM, Cisco, and Orange of France. There are a large number of companies in each link of the industrial chain (terminal hardware manufacturers, chip manufacturers, module gateway manufacturers, software manufacturers, system integrators, network operators). The openness of this technology makes competition and cooperation more difficult. The adequacy has promoted the rapid development and ecological prosperity of LoRa.
3. LoRaWAN network topology
The LoRaWAN network is a typical Mesh network topology. In this network architecture, the LoRa gateway is responsible for data aggregation and connecting terminal devices and back-end cloud data servers. The gateway and server are connected via TCP/IP network. There is two-way communication between all nodes and the gateway. Considering the battery-powered situation, the terminal node usually sleeps. When there is data to be sent, it wakes up and then sends the data.
Therefore, using LoRa technology, we are able to obtain longer transmission distances with low transmit power. This low-power wide-area technology is necessary for large-scale deployment of wireless sensor networks.
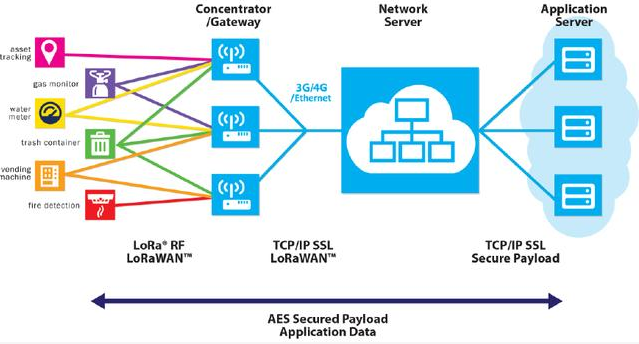
4. Introduction to LoRaWAN protocol
LoRaWAN is a low-power wide area network communication protocol based on the open source MAC layer protocol released by the LoRa Alliance. It mainly provides local, national or global network communication protocols for battery-powered wireless devices.
LoRaWAN? defines the communication protocol and system architecture of the network, and the LoRa® physical layer enables long-distance communication links. Designed from the bottom up, LoRaWAN optimizes LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Network) for battery life, capacity, distance and cost. An overview of the LoRaWAN specifications for different regions is given, as well as a high-level comparison of the different technologies competing in the LPWAN space.
I won’t introduce the advantages and disadvantages of LoRa one by one here. Anyone who knows a little bit about this network, I believe you all know it. If you don’t want to Baidu, you can directly click this link: Short-distance wireless communication networking technology to understand the advantages and disadvantages of LoRa. . This concludes the introduction of ” Lora technical principles “, I hope it will be helpful to you!