We often receive messages like this on WeChat: “A batch of IoT cards are currently shipped at a very low price, 300M/year/2 yuan/card.” Seeing this, a series of question marks emerged, what is the Internet of Things card? Why are rates so low? Can the ubiquitous touts believable?


1. What is an IoT card?
The Internet of Things card refers to connecting any item to the Internet through radio frequency identification (RFID), infrared sensors, global positioning systems, laser scanners and other information sensing equipment according to the agreed agreement for information exchange and communication. A network that realizes intelligent identification, positioning, tracking, monitoring and management.


Simply put, the Internet of Things card is a traffic card provided by the three major operators (China Mobile, China Unicom, and China Telecom) and based on the Internet of Things private network to meet the networking and management of smart hardware and the mobile information application needs of group companies. .
To put it simply, it is a card for networking electronic hardware. It cannot make calls and focuses on surfing the Internet, so it is equivalent to a data card. It should be noted that the IoT card is aimed at IoT enterprises, not individuals. The subject of real-name card application needs to be the legal person of the operating company.
1. The operator has a dedicated number segment
The three major operators use their own dedicated number segments for the Internet of Things, support basic communication services including SMS, wireless data and voice through dedicated network element equipment, and provide users with intelligent connection services such as independent communication connection management and terminal management.

2. Classification of IoT cards
IoT cards are divided into MS cards and MP cards. Normally, MS cards are only used for front-loading in production, while MP cards may be used for both front-loading and post-loading.
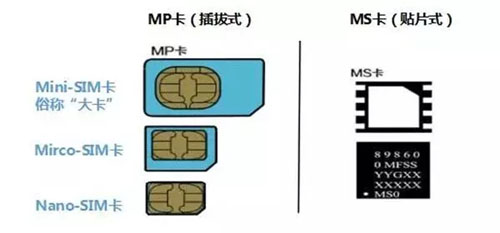

MP card, a plug-in card, looks similar to a SIM card. It can be used in extremely low or extremely high temperature environments and adapt to different harsh external environments. And because of its low cost and easy installation, it has a wider range of applications.
MS card, SMD card, is generally welded on the equipment and used for pre-production assembly. Because of its small size, earthquake resistance, high temperature resistance, and long life, it is often used in vehicle front-mounted installations, smart meter readings, and wearable devices.
2. What is the difference between IoT card and SIM card?
We are familiar with mobile phone SIM cards, and most people regard IoT cards as pure data cards. IoT cards are usually charged according to traffic, and traffic rates are very small, so they are popular among dual-card and dual-standby users.
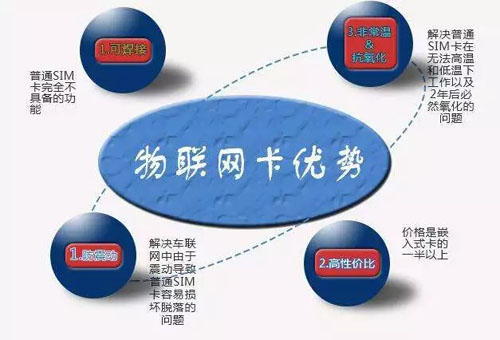

In addition to not being able to communicate via phone calls, what are the differences between IoT cards and SIM cards?
The materials are different. The plug-in IoT card and the ordinary SIM card are the same in size and shape. However, the ordinary SIM card is used in the mobile phone environment, and the relative temperature and humidity are relatively ideal. It is usually packaged with PVC, ABS and other materials; Because the SIM cards are used in Internet of Things devices, and some are used outdoors and other environments, the materials used are more durable than ordinary SIM cards.


- Ordinary SIM cards are mainly plug-in MP cards, but the IoT card adds an embedded MS card, which uses welding technology and is placed in front of the IoT device. It has good seismic resistance and ensures stable data transmission.
- Ordinary SIM cards do not require a management platform, but IoT cards generally require an IoT card management platform. In the platform, you can check traffic usage, whether the device is online, recharge and other functions.
- Ordinary SIM cards have built-in STK menus, through which functions or applications can be used; IoT cards are mainly used for Internet access and have no other applications.
- Ordinary SIM cards use 11-digit numbers, while IoT cards use 13-digit numbers, and the number resources are more abundant.
3. How to use the IoT card?
The Internet of Things card is used by group enterprises and related professional fields. It is a package card that belongs to the category of “group customers”. Individual users cannot apply for group customer packages in the business hall. In addition, operators also sell them through IoT card suppliers through various channels.
Operators’ IoT card tariffs can be divided into three standards: national unified tariff standards, local regional tariff standards, and group customer tariff standards. Among these three standards, the group customer package is often the most cost-effective.
It should be noted that since IoT cards can also be used in mobile phone terminals, they are often issued by card dealers through group customer channels and sold on the market. Since this card does not have voice and call functions, the data rate is 3-4 times cheaper than ordinary SIM cards.
The IoT card is a traffic card issued by a group unit in a unified name. It is suitable for all types of terminal equipment and cannot be processed in real names. Therefore, IoT card vendors that require real-name registration generally do so to collect customers’ identity information and then resell it for personal use. To improve telecommunications security and prevent telecommunications fraud, we would like to remind everyone to pay more attention to such traps.
4. Where are IoT cards used?
IoT cards are widely used in mobile media, monitoring and surveillance, medical health, Internet of Vehicles, wearable devices, smart watches, wireless POS machines and many other fields.
1. Wireless POS machine
The application on wireless POS machines is early and very mature. Traditional POS machines require communication through telephone lines, so they can only be installed near the telephone. They cannot be moved due to cable restrictions, and they are large. After adding the IoT card to the POS, you can get rid of these constraints and take it with you like a mobile phone, achieving mobility and making it more convenient to use. Since the POS machine generates very little data by swiping the card, and the traffic fee is also low, it can be used for one year for about 30 yuan, achieving greater popularity.


2. Wearable devices
Through data linking through the Internet of Things card, wearable devices will no longer need to use mobile phones to connect to the Internet anytime and anywhere. For example, the elderly or young wear devices with positioning functions and can achieve GPS positioning through the Internet of Things card; wearable devices use the Internet of Things card to collect the user’s walking steps, walking distance, life trajectory, sleep quality, and physical health in real time. status data.


3. Shared bikes
In 2015, shared bicycles began to rise. Its GPS positioning function and scanning and unlocking functions are all realized through the Internet of Things card network. Take Mobike as an example, it has covered 170 cities around the world and has launched a total of nearly 8 million bicycles. Its core technology is the Internet of Things card. Each bicycle is equipped with a “Beidou GPS” multi-mode satellite navigation chip and a mobile Internet of Things chip, which can monitor the location and status of the bicycle in real time. Previously, Mobike announced a strategic cooperation with Sichuan Mobile and ordered 1 million IoT cards issued by Sichuan Mobile.


4. Internet of Vehicles
After a car is equipped with an IoT card, the on-board automatic diagnosis system can collect the operating conditions of the vehicle’s brakes, tires, engines and other components in real time, providing car owners with various car data to ensure safe travel. IoT cards are also commonly used in vehicle navigation, driving recorders, smart central controls, etc.


5. Chaos in the IoT card market
From the above, it seems that IoT cards should be innovators that actively promote the development of IoT, but they are abused and sold by speculators.
It is understood that there are currently more than 400,000 wool workers engaged in “black production” in my country. If peripheral personnel in related industries are included, the total number exceeds 1.6 million. For the Wool Party, their most important profit-making tool is mobile phone cards. However, with the tightening of the real-name mobile phone policy, my country’s mobile phone numbers have almost achieved 100% real-name registration. Regular mobile phone SIM cards are becoming increasingly difficult to obtain, and many people are targeting IoT cards.


At present, about 80% of the mobile phone cards used by the Wool Party are IoT cards. For them, they choose IoT cards because of their low fees, no monthly rent, and the ability to receive business platform text messages.
According to surveys, just one “black card” can bring nearly 100 yuan in income to the Wool Party, and the annual losses caused by IoT cards alone exceed 3.2 billion yuan. For many start-up companies, the Wool Party cannot be ignored. There is, this group can use IoT cards to easily bring a company to life, and it can also make a company collapse quickly.
The IoT cards are aimed at corporate customers, so why do WeChat groups often receive messages such as “A batch of IoT cards are currently shipped at a very low price, 300M/year/2 yuan/card”? According to reports, the threshold for obtaining an IoT card is very low, and it can be easily obtained as long as there are channels.
IoT cards easily flow into the market and disrupt the market environment wantonly, so relevant policies are also tightened. For example, Taobao restricts the sale of IoT cards and does not allow them to be sold separately. Merchants can give away IoT card services with hardware devices (such as Mifi, car machines, etc.), and service providers who give away IoT cards with hardware devices must meet certain conditions. .
6. Conclusion
It is estimated that by 2025, there will be more than 25 billion connected devices worldwide. As a bridge connecting smart hardware and IoT networks, IoT cards are very popular in various fields such as smart security, smart homes, and smart alarms. At present, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology has not explicitly regulated IoT cards. However, with the rapid development of the IoT industry, IoT cards, as the core of the IoT, will surely become the focus of supervision.