With the continuous development of IoT technology, NB-IoT and Zigbee, as two important wireless communication technologies, have extensive applications in the field of IoT. Although they are both technologies used for communication between IoT devices, there are clear differences in many aspects.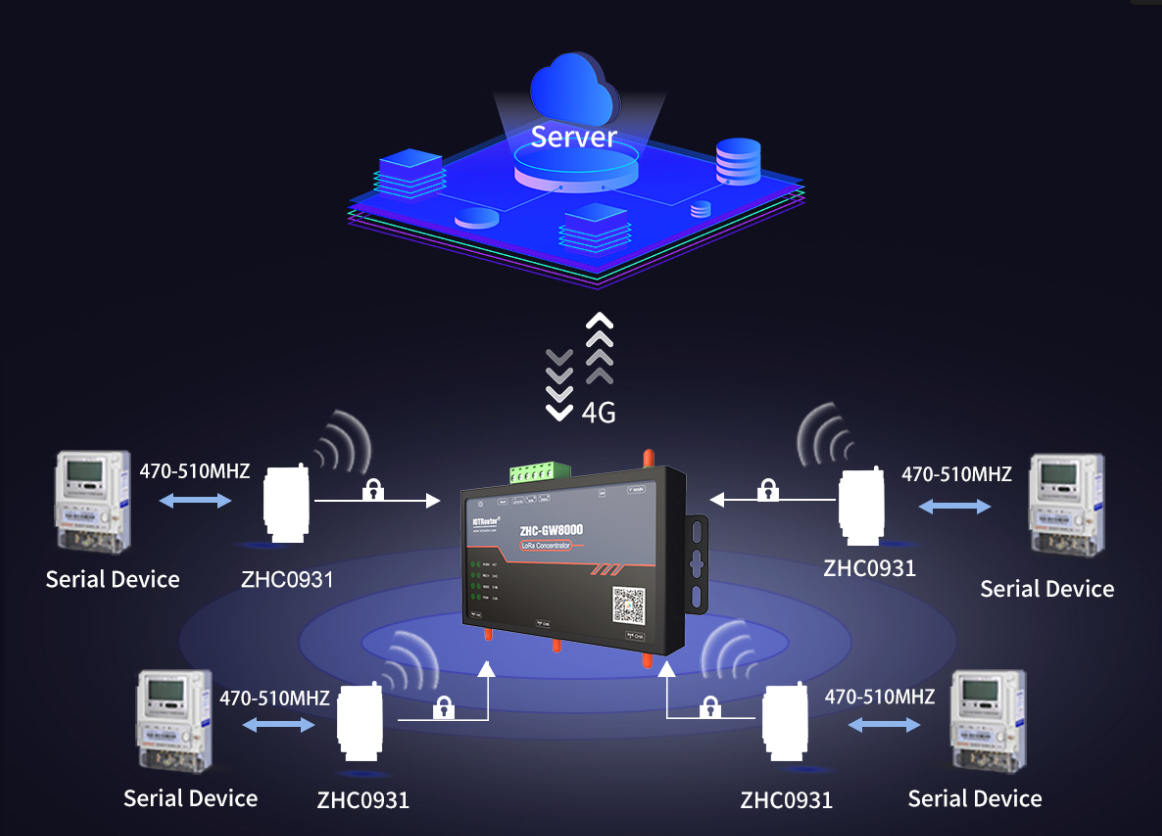 First, let us introduce NB-IoT. NB-IoT is the abbreviation of Narrow Band Internet of Things. It is a low-power wide area network (LPWAN) technology designed to provide long-distance connections for low-power devices. NB-IoT can provide good coverage both indoors and outdoors, and has lower power consumption and higher connection stability. Therefore, it has a wide range of applications in smart cities, smart buildings and other fields. Zigbee is a low-power, short-range wireless communication technology operating in the 2.4GHz frequency band, and is suitable for home automation, smart home and other scenarios.
First, let us introduce NB-IoT. NB-IoT is the abbreviation of Narrow Band Internet of Things. It is a low-power wide area network (LPWAN) technology designed to provide long-distance connections for low-power devices. NB-IoT can provide good coverage both indoors and outdoors, and has lower power consumption and higher connection stability. Therefore, it has a wide range of applications in smart cities, smart buildings and other fields. Zigbee is a low-power, short-range wireless communication technology operating in the 2.4GHz frequency band, and is suitable for home automation, smart home and other scenarios.
Secondly, from the perspective of technical characteristics, NB-IoT and Zigbee are also very different. As a cellular network technology, NB-IoT uses narrow-band modulation, supports a large number of connections and low-speed transmission, and is suitable for application scenarios with low power consumption, wide coverage, and low speed. Zigbee is a self-organizing mesh network technology specially designed for low power consumption, low data rate, and high cost-effectiveness. It has good applications in small areas such as homes and buildings. In addition, NB-IoT is also different from Zigbee in terms of frequency band usage, network topology, etc.
Finally, let us compare the differences between the two in application scenarios. Because NB-IoT has good coverage and connection stability, it has been widely used in smart cities, smart agriculture, environmental monitoring and other fields. Due to its low cost and low power consumption, Zigbee is more widely used in small-scale, intensive device connection scenarios such as home automation and building automation.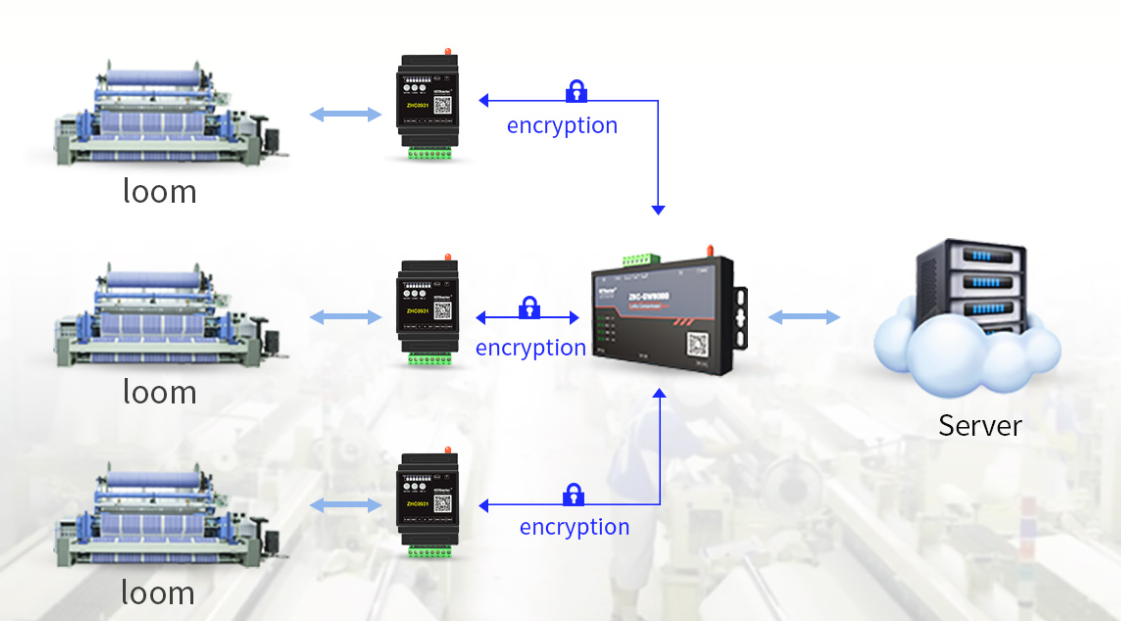
In general, NB-IoT and Zigbee, as important communication technologies in the field of Internet of Things, each have unique characteristics and application scenarios. Through the introduction of this article, I hope readers can have a clearer understanding of the differences between the two so that they can choose the appropriate technical solution in actual IoT projects.