The so-called driver actually refers to the power supply of LED lamps. From a professional perspective, it can be divided into 4 types: namely “resistance-capacitance type, constant voltage type, constant current type and constant current and constant voltage type”. The following is a brief introduction to the characteristics and configuration requirements of these four power supplies:
1. Resistor-capacitance step-down type
The resistance-capacitance step-down power supply is characterized by simple structure and low cost. Its schematic diagram is as follows.
The buck capacitor in the circuit is the core component of the entire circuit, and its capacity is generally between a few tenths and several microfarads. Its capacitive reactance can be calculated by the following formula:
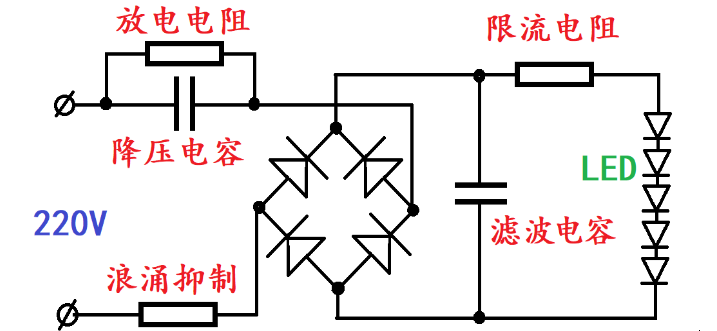
Xc=1/ωC is obtained. In the formula, C is the capacitance, unit F, and ω is a fixed value ≈ 314 in a 50Hz AC circuit. The function of the parallel resistor on the capacitor is to discharge. It can not only prevent damage to maintenance personnel after a power outage, but also prevent the superposition of the residual electricity of the capacitor and the voltage when power is turned on again, causing an impact on the subsequent circuits. The value is generally between a few hundred KΩ and 1MΩ. Surge suppression resistors generally range from a few Ω to tens of Ω.
The main disadvantage of resistor-capacitor voltage reduction is that it is susceptible to surge voltage impact, and there is also “stroboscopic”. Especially when switching or unplugging the power supply, the LED lamp beads may be easily injured. In addition, since the output end of the resistor-capacitor step-down is directly connected to the high-voltage input end, it can easily bring danger to maintenance. When using it to drive low-voltage LED lamp beads, the filter capacitor will also “fire” due to the open circuit of the load. For example, if the working voltage of the lamp bead is 50V and a capacitor with a withstand voltage of 80V is used, once the load is opened, the voltage on the capacitor will rise to more than 300V, causing breakdown.
Therefore, resistor-capacitor voltage reduction is only used in simple lamps with low cost, low power and little change in load current, or in high-voltage LED light strips and light strings.
2. Constant voltage drive
The main objects of constant voltage drive are light bars, light strips and guardrail tubes for landscape lighting and auxiliary lighting.
Constant voltage drive mainly has two specifications: 12ⅴ and 24ⅴ. Taking the 12V load as an example, its basic structure is that every three lamp beads are connected in series and a current-limiting resistor is added to form a group. A light bar or strip is composed of several such small units connected in parallel. Therefore, the unit connection can be used as a node according to the actual site conditions, and the total length can be intercepted arbitrarily, which is very convenient.
As a power supply, since the output voltage is fixed, as long as the power and wiring allow, the number of meters of lamp (root) strips a power supply can be determined according to the site conditions. Of course, each manufacturer has clear regulations on how many meters a power supply port can carry. As long as it is used as the upper limit and does not exceed it, it will be fine.
However, if constant current power supply is used, the problem will be artificially complicated, because the current and voltage ranges must be precisely matched. If one meter (root) is removed or broken, it will affect other parts. The constant voltage power supply is very “tolerant” to the load. As long as it is not overloaded, adding 1% or 90% load to the power supply will not affect the normal operation of the load. Furthermore, the light strips are auxiliary lighting, and the lamp beads do not operate at maximum power, so the driving mode of constant voltage + current limiting resistor will not have a significant impact on the life of the lamp beads.
3. Constant current power supply
Constant current power supply is the most widely used driving method for LED lighting fixtures. Because LEDs are nonlinear components, small voltage changes will cause large current changes. Moreover, LED lamp beads used for lighting basically work near the maximum power, so enhancing heat dissipation and keeping the current constant are the main ways to extend the life of the lamp beads. .
The output voltage of a constant current power supply is not a fixed value, but a range. This is also the main basis for us to identify constant current power supplies.
Because the internal resistance of the LED will become smaller when the temperature rises, if you want to keep the current constant, you must reduce the voltage; conversely, when the temperature is low in winter, the internal resistance of the LED will increase, and the current will also decrease. To keep the current constant, the voltage must be increased. This requires that the output voltage of the constant current drive must be continuously adjusted as the internal resistance of the LED changes, and cannot be fixed.
When selecting a constant current drive, both current and voltage must be considered. There is no need to elaborate on the current, as long as it matches the light source. Regarding voltage, be sure to keep the voltage of the light source within the range of the power supply output voltage. For example, the voltage of 10 strings of white LEDs is generally around 31V, and a voltage of 28~38v is sufficient. But be sure not to touch the upper and lower limits of the voltage range, otherwise the protection function of the power supply will take effect and cause the lamp beads to flicker.
4. Constant current and constant voltage power supply
First of all, let me explain that the so-called “constant current and constant voltage” power supply does not maintain a constant current and achieve a constant voltage power supply. Instead, it can automatically switch between constant current and constant voltage states according to load changes, that is to say, constant current is not constant voltage, and constant voltage is not constant current.
This kind of power supply usually does not label the output voltage range, but only labels the two parameters of voltage and current, which sometimes makes it difficult to distinguish it from a constant voltage power supply.
In essence, a constant current and constant voltage power supply is a constant current power supply with a rigid voltage upper limit. For example, when the internal resistance of the LED lamp bead increases, in order to maintain the current constant, the output voltage will begin to rise. If the current never reaches the specified value, the output voltage of the ordinary constant current power supply will rise to the highest level and activate the protection function, and the lamp bead will begin to flash. The difference between this kind of power supply is that when the voltage rises to the nominal value, it will not increase anymore, but will automatically switch to a constant voltage state.
Keywords in this article: full network module