Internet of Things, abbreviated as IoT, is an important part of the latest generation of information technology and an important development stage in the “information age”.
The Internet of Things is widely used in the integration of networks through communication sensing technologies such as intelligent sensing, identification technology and ubiquitous computing. It is therefore known as the third wave of the development of the world’s information industry after computers and the Internet.
This article will let you know:
(1) From the perception layer, network layer, platform layer and application layer of the Internet of Things;
(2) Clear away the fog of the concept of the Internet of Things in simple and easy-to-understand terms.
1. Overview of the Internet of Things
●The concept of Internet of Things was first proposed by MIT in the United States in 1999. The early Internet of Things refers to the concept of Internet of Things based on RFID.
(Radio Frequency Identification) technology and equipment are combined with the Internet according to the agreed communication protocol to make item information real
It realizes intelligent identification and management and realizes the interconnection, exchange and sharing of item information.
●Information sensing through QR code reading equipment, radio frequency identification (RFID) devices, infrared sensors, global positioning systems and laser scanners
The device, according to the agreed protocol, connects any item to the Internet for information exchange and communication to achieve intelligent identification, positioning,
A network that is tracked, monitored and managed.
——International Telecommunication Union (ITU)
●Internet of Things-IoT is the Internet where things are connected.This has two meanings: the core and foundation of the Internet of Things
It is still the Internet, a network that is an extension and expansion based on the Internet; secondly, its user end extends and expands to ugly items and
Information exchange and communication are carried out between items, that is, things are related to each other.
–Baidu Encyclopedia
2. Development of Internet of Things
(1) The origin of the Internet of Things is the “Truui Coffee Pot Server” Coke vending machine.
(2) In 2005, the International Telecommunication Union ITU released the “ITU Internet Report 2005: Internet of Things” at the World Summit on the Information Society (WSIS) in Tunisia, which applied the concept of “Internet of Things”. At this time, the definition and scope of the Internet of Things Things have changed and it is no longer just IoT based on RFID technology.
(3) In November 2008, IBM proposed the concept of “Smart Planet”.
(4) In August 2009, “Perceiving China” pushed the research and application development in the field of Internet of Things in my country to a climax. Wuxi City took the lead in establishing the “Perceiving China” research center. The Chinese Academy of Sciences and Wuxi Jiangnan University also established a national The first physical IoT factory academy.
(5) In April 2013, the German government formally proposed the “Industry 4.0” strategy at the Hannover Industrial Fair in April 2013, aiming to improve the intelligence level of the manufacturing industry. Its technical basis is network entity systems and the Internet of Things.
(6) On May 8, 2015, “Made in China 2025” was signed and released. As the first ten-year program of the China Power Strategy, the in-depth implementation of “Made in China 2025” has further accelerated the development of big data, big data, and the Internet of Things. Applications in industrial manufacturing.
3. Common applications of the Internet of Things
(1) The Internet of Things is common and closely related in our lives, such as shared bicycles, queuing up, smart parking, and smart homes all have the Internet of Things.

(2) Division of IoT access technology application scenarios
| Kenmerken | Industrial application | |
|
4G/5G LTE-V |
Transmission rate >10M bps; higher power consumption |
Internet of Vehicles, video surveillance, smart capable machine… |
|
ikB GPRS |
Transmission rate |
|
Wearable, vehicle dispatching, electronics Advertising, wireless ATM… |
| N B-IoT | Transmission rate |
|
Remote meter reading, public utilities, Agriculture, forestry, fishery and animal husbandry…… |
4. Hierarchical division of the Internet of Things
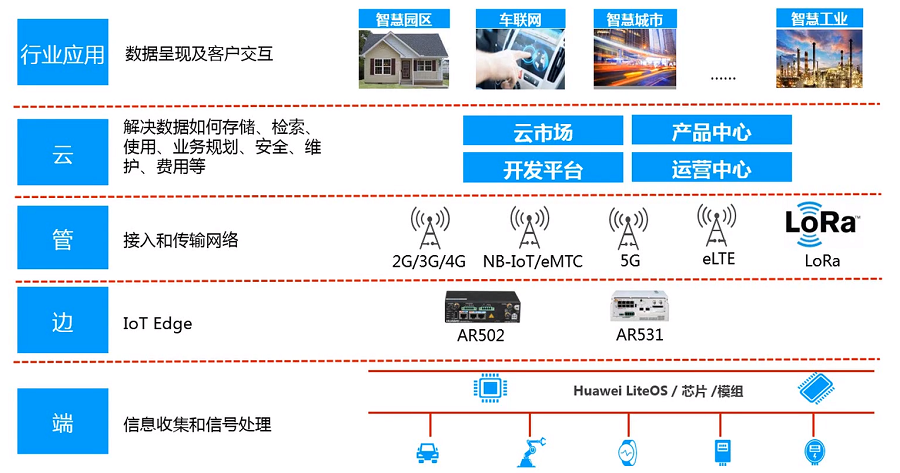
5. IoT connection management platform
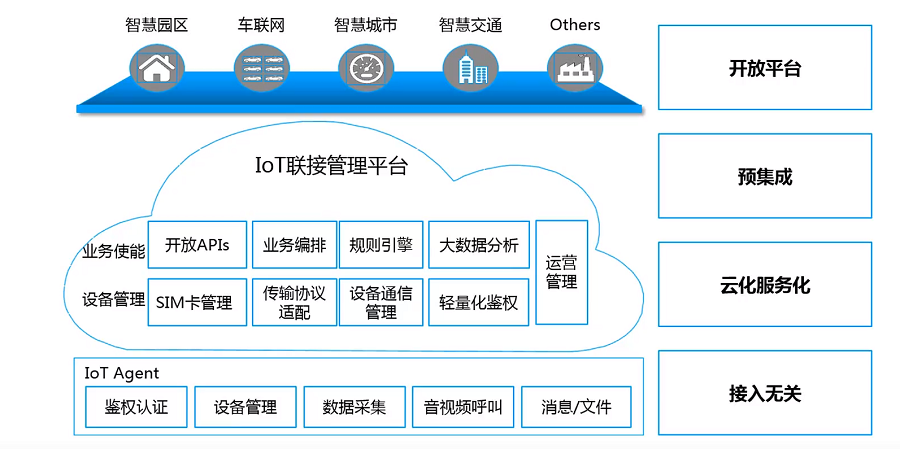
6. Internet of Things Products
(1) Sensors. There are many types of sensors, such as temperature and humidity sensors, pressure sensors, water level sensors, temperature sensors, etc. You should know what they are used for when you hear the name.
(2) Data transmission equipment – also called data transmission terminal, which can also be divided into 2 major categories. DTU (mainly used for simple transparent transmission of data). RTU (while supporting data transparent transmission, it also supports analog acquisition and some logic control, such as switch control, etc.)
