Niubility technology in NB-IoT
2020-05-27 17:15:05 Azir 17
NB-ioT technology has always attracted much attention. What are the key features that make it so popular? (Super coverage, ultra-low cost, ultra-low power consumption, ultra-large connection, SC-FDMA, OFDMA) Behind these characteristics , and what technologies it includes, this article will take everyone to understand NB-ioT.
NB-IOT physical layer
First, start from the bottom. The system bandwidth of NB-ioT is 180KHz. The uplink technology uses SC-FDMA, which is a continuous modulation and demodulation technology of subcarriers and is also the mainstream technology used for LTE uplink. Generally, there are two transmission technologies for uplink transmission: single carrier and multi-carrier.
Single-tone: Indicates that the terminal device only occupies one subcarrier for uplink data transmission.
Multi-tone: Multi-tone means that multiple sub-carriers can be occupied for uplink data transmission.
Under the premise of the same power, Single-Tone has a higher power spectral density gain than Multi-tone.
NB-ioT uplink supports Single-Tone and Multi-tone transmission, where Single-tone is a necessary function for terminal equipment, and Multi-tone is an optional function.
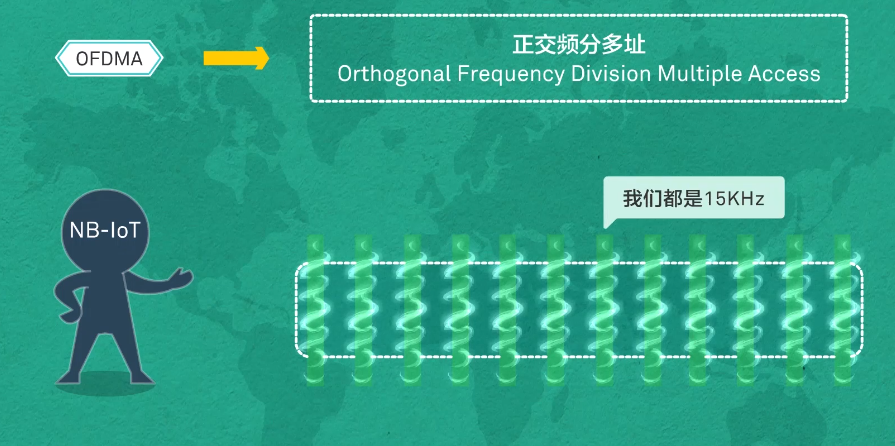
NB-ioT downlink technology uses OFDMA, which is an evolution of OFDM technology and combines OFDMA and OFDM technologies. OFDMA uses OFDM to subcarrier the channel, and then loads transmission data on some subcarriers.
NB-IOT uses OFDMA to divide the 180KHz bandwidth into 12 subcarriers. 15KHz per subcarrier.
Compared with LTE, in order to reduce implementation complexity, NB-ioT streamlines unnecessary physical channels.
There are only three physical channels and two reference signals in the downlink, and there are only two physical channels and one reference signal in the uplink.
The physical channel of NB-ioT has achieved increased coverage, reduced costs, and reduced power consumption by reducing the target rate, transmitting multiple times, and adopting low-order modulation methods.
NB-ioT network deployment method
After understanding the underlying physical layer, let’s take a look at how the NB-ioT network is built and deployed! NB-ioT is built on the cellular mobile network and supports the smooth evolution of the current LTE standard.
And according to the needs of different operators, it supports flexible frequency band deployment. NB-ioT supports three deployment modes, namely: independent deployment (Stand-alone), guard-band deployment (Guard-band), and in-band deployment (Inband).
Independent deployment mode: A separate frequency band can be used, suitable for re-cultivation of GSM frequency bands.
Guard band deployment mode: You can utilize edge useless frequency bands in the LTE system.
In-band deployment mode: Any resource block in the middle of the LTE carrier can be utilized.

From the unique physical layer foundation of NB-IOT and its flexible deployment method, we can find that NB-IOT is different. Differentiation must be unique. What are the key features of NB-IOT? The following article explains in detail.