The IoT gateway is like the central brain of human beings. It transmits, calculates and processes data on what is seen and heard by the five senses. It also helps break through vertical barriers, realize cross-border processing, and fully tap the true potential of the Internet of Things.


1. What is a gateway?
A gateway is a computer system or device that does the heavy lifting. A gateway is a translator between two systems that use different communication protocols, data formats or languages, or even completely different architectures. Unlike bridges that simply convey information, gateways repackage received information to suit the needs of the destination system. At the same time, the gateway can also provide filtering and security functions.
2. What is the gateway of the Internet of Things?
In the architecture of the Internet of Things, a bridge is built between the two different levels of the perception layer and the network layer, which is the “Internet of Things gateway. It can realize both WAN interconnection and LAN interconnection. In addition, the IoT gateway also needs to have device management functions. Operators can manage the underlying sensing nodes through the IoT gateway-apparaat, understand the relevant information of each node, and achieve remote control.
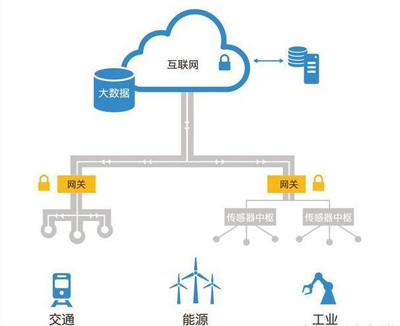

3. Characteristics of IoT gateway
Comprehensive perception, that is, using RFID technology, sensor access, QR codes, etc. to obtain object information at any time;
Reliable transmission, through NB-IoT or LoRa networking, and integration with the Internet, information can be transmitted accurately in real time;
Intelligent processing uses cloud computing, fuzzy recognition technology, edge computing technology, etc. to analyze and preprocess data to implement intelligent control of objects.
4. Functions of IoT gateway
1. Conversion of protocol
Protocol conversion from different sensing networks to access networks, uniformly encapsulating data in the standard format of the lower layer, ensuring that the protocols of different sensing networks can be converted into unified data and signaling; parsing data packets sent by the upper layer into sensing signaling and control instructions that can be recognized by layer protocols.

2. Controllability and management capabilities
First, the gateway must be managed, such as registration management, rights management, status supervision, etc. The gateway implements the management of nodes in the subnet, such as obtaining the node’s identity, status, attributes, energy, etc., and remotely realizing wake-up, control, diagnosis, upgrade, and maintenance. Because the technical standards of subnets are different and the complexity of the protocols is different, the management capabilities of the gateways are different.

3. Data filtering function
Sometimes, sensors/devices generate large amounts of data, which puts a lot of pressure on the system and increases transmission and storage costs accordingly. Typically in this case, only a small portion of the data is valuable and the rest is filtered out. For example, the camera does not need to send video data of the corridor. Gateways can pre-process and filter data generated by sensors/devices to reduce transmission, processing and storage requirements.
4. Extensive access capabilities
There are currently many technical standards for short-range communications. Standardization work for IoT-gateways is already underway at home and abroad, such as 3GPP and sensor working groups, to achieve interconnection and interoperability of various communication technology standards.

5. Conclusion
In the highly fragmented development stage of the Internet of Things, no standard can directly achieve unification like Qin Shihuang did, but the Internet of Things gateway can “save the country” to a certain extent.