Mobile communications are moving from the connection between people to the connection between people and things, and between things and things. The interconnection of all things is an inevitable trend. The connection requirements of the Internet of Things are very different from traditional cellular networks. Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT) technology, as an emerging technology in the field of Internet of Things, came into being under the application needs of the Internet of Things. Nowadays, NB-IoT technology is widely used in agriculture, industry, government and life. So what is the architecture of NB-IoT technology?
1. NB-IoT technology architecture diagram
The typical narrowband IoT architecture has three layers, which are the perception layer, network layer and application layer from bottom to top.
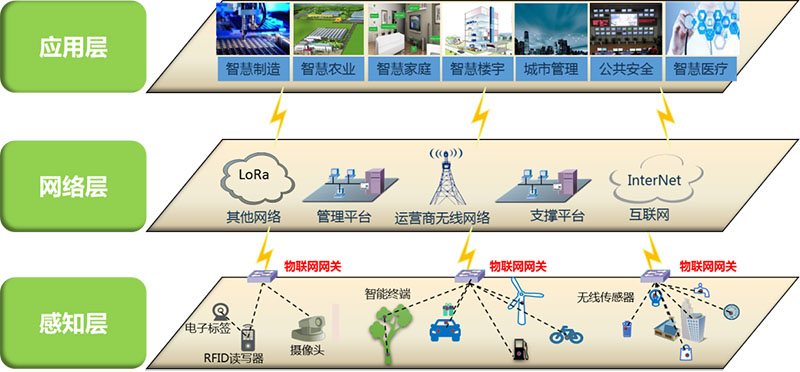

Perception layer: It is composed of various sensors, including temperature and humidity sensors, QR code tags, RFID tags, readers, cameras, infrared, GPS and other sensing terminals. The perception layer is the source of identifying objects and collecting information in the Internet of Things. If NB-IoT is compared to a human being, the perception layer is the sense organs such as eyes, nose, ears, and skin.
Network layer: It is composed of various networks, including the Internet, radio and television networks, network management systems and cloud computing platforms. It is the hub of the entire Internet of Things and is responsible for transmitting and processing information obtained by the perception layer. The narrowband IoT network layer is equivalent to the human nervous system, transmitting various signals.
Application layer: It is the interface between the Internet of Things and users. It combines with industry needs to realize intelligent applications of the Internet of Things. The application layer of the Internet of Things is equivalent to the human brain, responsible for analyzing and processing various data.
2. Advantages of NB-IoT technology
1. Wide coverage: NB-IoT has strong indoor coverage. In the same frequency band, NB-IoT has a gain of 20dB compared to the existing network, which is equivalent to increasing the coverage area by 100 times. It can not only meet the wide coverage needs in rural areas, but is also suitable for applications that require deep coverage such as factories, underground garages, and manhole covers.
2. Strong link: With the same base station, NB-IoT can provide 50 to 100 times the number of access points than existing wireless technologies. One sector can support 100,000 connections, supporting low latency sensitivity, ultra-low equipment cost, low equipment power consumption and optimized network structure. This means that we can place more devices in a space that is not too big without interfering with each other.
3. Low power consumption: NB-IoT module can work in 3 states to save power consumption. The maximum current consumption in PSM mode is 5uA, and in IDLE mode it is approximately 6mA. According to the simulation data of TR45.820, a 5Wh battery sends 200 bytes of data every day and is expected to last 12.8 years. Therefore, it can be used to develop various sensor monitoring equipment placed in remote areas of high mountain wilderness.
4. Low cost: NB-IOT does not need to rebuild the network, and the radio frequency and antenna are basically universal. Whether it is module cost, power supply, or communication operation costs, it is cheaper than other wireless terminals. With the development of NB-IoT, the expected price of a single connection module is no more than 5 US dollars, or even as low as 2 US dollars. Recently, China Telecom released its first NB-IoT annual package, which only costs 20 yuan.
3. NB-IoT technology application scenarios
NB-IoT technology can be widely used in wireless monitoring and early warning of computer rooms, machine station power, environmental monitoring systems, low-voltage distribution monitoring systems, power data monitoring systems, factory machinery and equipment, production line operating status monitoring systems, production information collection systems, etc. It is also used in real-time monitoring and early warning of environmental data in oil fields, oil wells, gas fields, steam pipelines, heating pipelines, water pump rooms, refrigeration, warehousing, agricultural greenhouses, breeding, etc.
