Understand the Internet of Things, the origin and development of the Internet of Things
2020-06-08 17:46:13 Azir 10
Speaking of the Internet of Things, are you both familiar and unfamiliar? Yes, from radio frequency technology that can be seen everywhere, to smart wearables, smart appliances, to the rapidly developing smart homes. Intelligent transportation, shared bicycles, drone transportation, smart medical care, etc. Behind these technological applications are the Internet of Things, but they are far from representing all of the Internet of Things.
The Internet of Things – this innovative Internet technology based on communication sensing technology and with unlimited potential for development, has set off the third wave of the development of the world’s information industry and will trigger huge changes in production and lifestyles. So how does communication sensing technology achieve such a powerful Internet of Things?
The origin of the Internet of Things
Antes de compreendermos a Internet das Coisas, temos de começar por estabelecer uma compreensão preliminar dos conceitos e tecnologias da Internet das Coisas. A razão pela qual a Internet das Coisas nasceu deve-se a uma cafeteira. Sim, ouviu bem. Tratava-se de uma vulgar cafeteira no andar de baixo do Laboratório de Informática Truy da Universidade de Cambridge, em 1991. A cafeteira não podia informar os cientistas lá em cima de forma inteligente. Para saber se o café estava bem passado, os cientistas inteligentes escreveram um conjunto de programas, instalaram uma câmara junto à cafeteira e utilizaram a tecnologia de captura de imagem da câmara do terminal para a transmitir ao computador do laboratório a um ritmo de 3 fotogramas/segundo, para que os cientistas pudessem verificar se o café estava passado em qualquer altura. Inesperadamente, esta "invenção de um preguiçoso" tornou-se o primeiro protótipo da Internet das Coisas.
Em 1993, como o primeiro caso do sistema X-windows. O incidente do "Truy Coffee Pot Server" também foi divulgado em linha. No que diz respeito às câmaras digitais em rede, para sermos precisos, o seu desenvolvimento no mercado, as aplicações técnicas e as várias expansões futuras da rede tiveram origem na "cafeteira Truui", a mais prestigiada do mundo.
Proposta do conceito de Internet das Coisas
Oito anos após o incidente da "cafeteira", ou seja, em 1999, Kevin Asthon propôs pela primeira vez o conceito de Internet das Coisas no Centro de Auto-ID do Instituto de Tecnologia de Massachusetts, nos Estados Unidos. Nesta altura, a Internet das Coisas refere-se apenas ao facto de se basear na tecnologia e no equipamento RFID. O protocolo de comunicação acordado é combinado com a Internet para realizar a identificação e a gestão inteligentes das informações dos artigos e realizar a interligação, o intercâmbio e a partilha de informações dos artigos para formar uma rede.
História do desenvolvimento da Internet das Coisas
Entering the 21st century, the Internet of Things has begun to develop rapidly, and its development process has gone through five stages.
(1) In 2005, the International Telecommunication Union ITU released the “ITU Internet Report 2005: Internet of Things” at the World Summit on the Information Society (WSIS) in Tunisia, which applied the concept of “Internet of Things”. At this time, the definition and scope of the Internet of Things Things have changed and it is no longer just IoT based on RFID technology.
(2) In November 2008, IBM proposed the concept of “Smart Planet”.
(3) In August 2009, “Perceiving China” pushed the research and application development in the field of Internet of Things in my country to a climax. Wuxi City took the lead in establishing the “Perceiving China” research center. The Chinese Academy of Sciences and Wuxi Jiangnan University also established a national The first physical IoT factory academy.
(4) In April 2013, the German government officially proposed the “Industry 4.0” strategy at the Hannover Industrial Fair in April 2013, aiming to improve the intelligence level of the manufacturing industry. Its technical basis is network entity systems and the Internet of Things.
(5) On May 8, 2015, “Made in China 2025” was signed and released. As the first ten-year program of the China Power Strategy, the in-depth implementation of “Made in China 2025” has further accelerated the development of big data, big data, and the Internet of Things. Applications in industrial manufacturing.
If the development process of the Internet of Things in the past 20 years and its future is divided, it can be roughly divided into three periods.

The first period is from the introduction of the concept of the Internet of Things to 2013. During this period, the Internet of Things has remained in the conceptual stage, and the equipment involved is only limited to “things” in the field of wireless radio frequency. The equipment involved is also limited to “things” in the field of wireless radio frequency. “thing”.
The second period is from 2014 to 2016. This period is marked by Google’s acquisition of Nest. The Internet of Things has evolved from wireless radio frequency devices to smart wearable and smart home devices.
The third period started in 2016 to the present. During this period, smart wearable devices and smart home devices have matured and entered daily life. At the same time, the maturity of IoT technology is climbing rapidly, providing a basis for the development of the IoT ecosystem. Build a good foundation for construction.
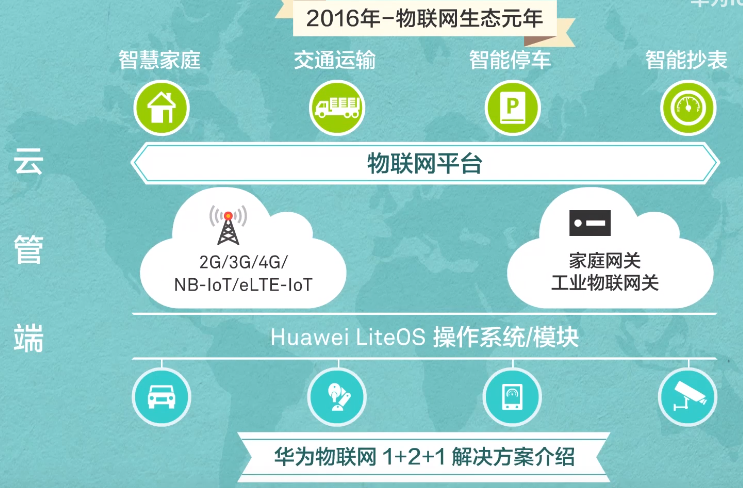
The freezing of the NB-ioT protocol marks a major breakthrough for the Internet of Things at the wide-area connection protocol level. If analyzed from the perspective of our cloud-pipe-end system logic system, the trend of the cloud-pipe-end closed loop completion of the Internet of Things has become more and more obvious. It is becoming more and more obvious, and we can even determine that 2016 is the first year of the Internet of Things ecosystem.
IoT layer
From the perspective of the cloud-pipe-end logical system, the levels of the Internet of Things can be simply divided into four levels: perception layer, network layer, platform layer, and application layer. (For example, our company – Chengdu Zongheng Intelligent Control is at the network layer, and the company’s business is the research and development and production of Internet of Things data transmission equipment). Let’s use a picture to describe these four layers.
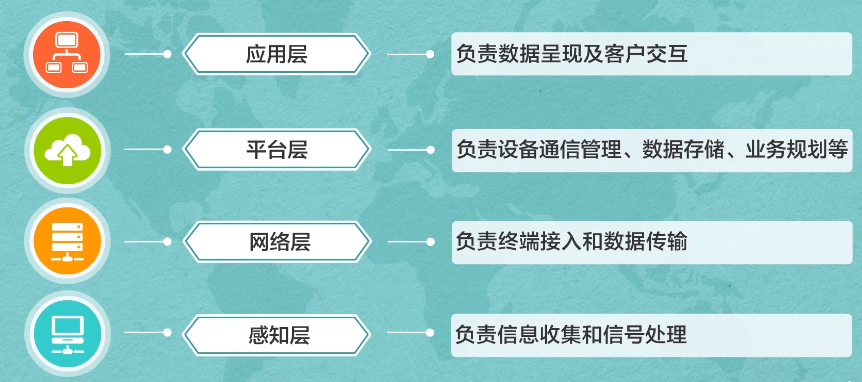
If further divided by vertical fields, the IoT industry applications can be simply divided into several major fields, such as industrial IoT, Internet of Vehicles, industrial IoT, smart home IoT, etc. The communication used in IoT application scenarios in different vertical fields Technology is not the same. Usually the Internet of Things will adopt corresponding communication technologies based on business needs.
Here we list the business applications of wide-area wireless communication technology, such as Internet of Vehicles and video surveillance. Businesses such as Internet of Vehicles and video surveillance have high communication transmission rate requirements, usually above 100Mbps, and will use 4G, 5G or LTE-V communication methods. These The communication method is characterized by low delay, fast speed, high power consumption and high cost.
For services such as smart wearable devices, elevator networking, electronic advertising, and wireless ATMs that we have access to daily, communication methods such as eMTC and GPRS are usually used. The characteristics of these communication methods are that the transmission rate is around 1Mbps, with low latency and low cost. And power consumption is also lower.
For services such as remote meter reading, smart parking, and smart agriculture, NB-IoT will be used for communication to meet the characteristics of low cost, low power consumption, low cost, and wide coverage.

Through this article, we understand the development history and hierarchical division of the Internet of Things. In the next article, we will talk about wireless communication technology and understand the Internet of Things from a technical perspective.
