The signal transmission range of a wireless data transmission module is an important indicator of its performance and applicability. The size of the signal transmission range directly affects the reliability of wireless communication and the limitations of application scenarios. In practical applications, many factors will affect the signal transmission range of wireless data transmission modules. This article will explore these factors and explain their specific impact on signal transmission range.
Transmitting power is one of the key factors that affects the signal transmission range of wireless data transmission modules. Transmission power refers to the strength of the signal transmitted by the wireless data transmission module. Generally speaking, higher transmit power provides greater transmission range. When the transmission power is large enough, the signal can overcome some attenuation and interference during transmission, making the transmission distance longer. However, it should be noted that different countries and regions have laws and regulations on the use of radio frequencies, stipulating the maximum allowable transmit power. Therefore, in practical applications, it is necessary to ensure that the transmit power is within the legal range.
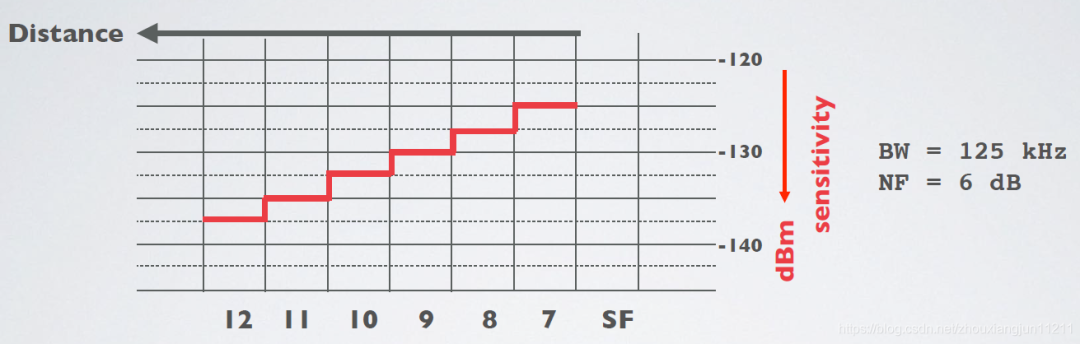
Receiving sensitivity also has an important impact on the signal transmission range of the wireless data transmission module. Reception sensitivity refers to the receiving device’s ability to effectively receive and decode signals. Higher reception sensitivity means that the receiving device can receive the signal at a greater distance. Receiving sensitivity is affected by the quality and technical level of the receiving equipment. Excellent receiving equipment usually has high sensitivity and can achieve reliable signal reception in weak signal environments.
Frequency is also an important factor affecting the signal transmission range of wireless data transmission modules. Different frequencies have different transmission ranges. Generally speaking, higher frequencies have a shorter transmission range because high-frequency signals are more likely to be blocked by obstacles during transmission. Low-frequency signals are relatively more penetrating and can pass through buildings and other objects better. Therefore, when selecting a wireless data transmission module, it is necessary to select the appropriate frequency according to the specific application scenario and environmental characteristics.
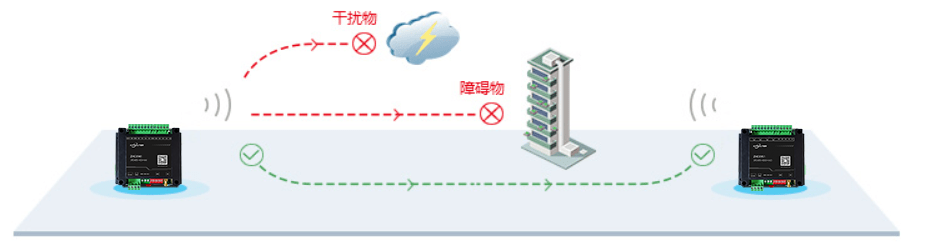
Obstacles and environmental conditions are also one of the important factors that affect the signal transmission range. Objects such as buildings, walls, mountains, and trees will reduce the range of the signal. These objects cause attenuation and obstruction to signal transmission, resulting in a reduction in signal transmission range. In particular, materials such as metal and concrete have a high shielding effect, which will significantly weaken the signal strength and transmission distance. In addition, electromagnetic interference sources in the environment will also interfere with signal transmission, further affecting the transmission range. Microwave ovens, radio equipment, etc. will produce electromagnetic radiation, which may interfere with the signal transmission of the wireless data transmission module.
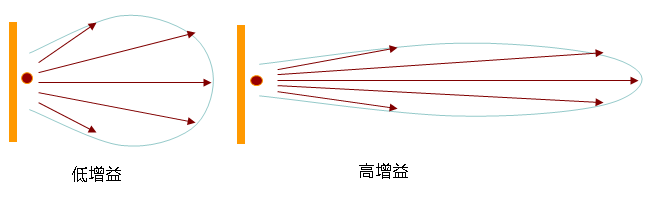
The performance and design of the antenna also play an important role in signal transmission range. The antenna is an important part of the wireless data transmission module and is responsible for transmitting and receiving signals. The gain and directivity of the antenna determine the radiation range and coverage direction of the signal. Using a high-gain antenna can expand the signal transmission range and enhance the signal strength and penetration. In addition, choosing the appropriate antenna type and installation location can also optimize signal transmission.
Other wireless devices and signals present in the environment will also affect the signal transmission range of the wireless data transmission module. These interfering signals may come from other devices or radio wave radiation in the same frequency band. This interference can reduce signal reliability and transmission distance, especially in environments with crowded spectrum. Therefore, when choosing the frequency band to use, it is necessary to avoid frequency conflicts with other devices to reduce the impact of interference on the signal transmission range.
Resumir
To sum up, the signal transmission range of the wireless data transmission module is affected by many factors. In practical applications, these factors need to be comprehensively considered and appropriate wireless data transmission modules and related equipment selected according to specific needs to ensure reliable signal transmission and meet the needs of specific application scenarios.