“Internet of Everything” is no longer just a fantasy. Nowadays, partial Internet of Things has been realized in many practical application scenarios, such as smart transportation, smart buildings, smart agriculture, industrial automation, etc. The Internet of Things is the field with the most market prospects in the next ten years, and related wireless communication technologies are gradually emerging.


Among the communication technologies that implement the Internet of Things, GPRS, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, ZigBee, NFC, etc. are the most widely used wireless technologies. In addition to these, there are many wireless technologies that work quietly in their respective suitable scenarios and play an indispensable role. This article will introduce ten common IoT wireless communications and help you understand the real IoT industry.
Advantages, disadvantages and application scenarios of the top ten communication technologies of the Internet of Things
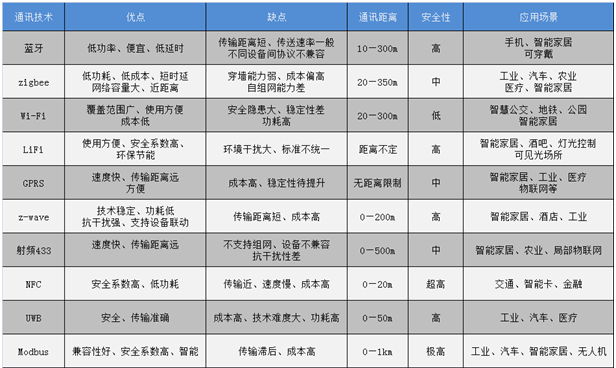

1. Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a wireless technology standard that enables short-distance data exchange between fixed devices, mobile devices and building personal area networks. Bluetooth can connect multiple devices and overcome the problem of data synchronization. Bluetooth technology was originally created in 1994 by telecommunications giant Ericsson. Today, Bluetooth is managed by the Bluetooth Technology Alliance, which has more than 25,000 member companies around the world, which are distributed in multiple fields such as telecommunications, computers, networks, and consumer electronics.
The characteristics of Bluetooth technology include the use of frequency hopping technology to resist signal fading; fast frequency hopping and short packet technology can reduce co-channel interference and ensure transmission reliability; forward error correction coding technology can reduce the impact of random noise during long-distance transmission; Use FM modulation to reduce the complexity of equipment, etc. Among them, the core specification of Bluetooth is to provide two or more piconet connections to form a distributed network, allowing specific devices to automatically play the roles of master and slave in these piconets at the same time. The Bluetooth master device can communicate with up to seven devices in a micronet. The devices can switch roles through protocols, and the slave device can also be transformed into the master device.
2. ZigBee
Different from Bluetooth technology, ZigBee technology is a short-distance, low-power consumption, cheap wireless communication technology. It is a wireless network protocol for low-speed short-distance transmission. The name comes from the eight-figure dance of bees, because bees rely on the “dance” of flying and zig-zagging wings (bee) to communicate the location of pollen to their companions. That is to say, bees rely on this method constitutes the communication network in the group.
ZigBee is characterized by short distance, low complexity, self-organization, low power consumption, and low data rate. The ZigBee protocol is divided into physical layer, media access control layer, transport layer, network layer, application layer, etc. from bottom to top. Among them, the physical layer layer and media access control layer follow the provisions of the IEEE 802.15.4 standard. ZigBee technology is suitable for automatic control and remote control fields and can be embedded in various devices.
3. Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi is very common in our lives. Almost all public places in first-tier cities are equipped with wireless networks. This is due to its low cost and transmission characteristics. Wi-Fi is a technology that allows electronic devices to connect to a wireless LAN, usually using the 2.4G UHF or 5G SHF ISM radio frequency band. Connections to wireless LANs are usually password-protected; but can also be open, allowing any Devices within WLAN range can connect.
Since the frequency bands of wireless networks do not require any telecommunications operator license worldwide, WLAN wireless devices provide a wireless air interface with extremely low cost and extremely high data bandwidth that can be used worldwide. Users can quickly browse the web within the Wi-Fi coverage area and answer and make calls anytime and anywhere. With the Wi-Fi function, we can make long-distance calls, browse the web, send and receive emails, download music, transfer digital photos, etc., without worrying about slow speeds. and high cost issues.
Wireless networks are increasingly used in handheld devices, and smartphones are one of them. Unlike Bluetooth technology that was previously used on mobile phones, Wi-Fi has larger coverage and higher transmission rates, so Wi-Fi mobile phones have become a fashion trend in the mobile communications industry in 2010.
4.LiFi
LiFi is also called visible light wireless communication. It is a new wireless transmission technology that uses the visible light spectrum for data transmission. It was invented by Professor Harald Haas, chairman of the Department of Mobile Communications at the School of Electronics and Communications at the University of Edinburgh in the UK and a German physicist. LiFi uses already laid equipment to form a device similar to a WiFi hotspot by implanting a tiny chip on the light bulb, allowing terminals to access the network at any time.
The biggest feature of this technology is that it transmits data by changing the flicker frequency of the room lighting. As long as the lights are turned on indoors, the Internet can be accessed without WiFi. It has broad application prospects in smart homes in the future.
5.GPRS
We can say that we are very familiar with GPRS. It is a mobile data service available to GSM mobile phone users and belongs to the data transmission technology in the second generation of mobile communications. GPRS can be said to be the continuation of GSM. GPRS is different from the previous continuous channel transmission method. It is transmitted in packets. Therefore, the cost borne by the user is calculated based on the unit of transmitted data, rather than using the entire channel. In theory, it is more Cheap.
GPRS is a technology between 2G and 3G, also known as 2.5G. It lays the foundation for a smooth transition from GSM to 3G. With the development of mobile communication technology, 3G, 4G, and 5G technologies have been developed, and GPRS has gradually been replaced by these technologies.


6. Z-Wave
Z-Wave is an emerging radio frequency-based, low-cost, low-power consumption, high-reliability, short-distance wireless communication technology suitable for networks. It is a wireless networking specification led by the Danish company Zensys. The operating frequency band is 908.42MHz (United States) ~ 868.42MHz (Europe), using FSK (BFSK/GFSK) modulation method, and the data transmission rate is 9.6 kbps, which is suitable for narrow broadband applications.
As the communication distance increases, the complexity, power consumption and system cost of the device are increasing. Compared with various existing wireless communication technologies, Z-Wave technology will be the lowest power consumption and lowest cost technology, effectively Driving low-rate wireless personal area networks.
7. RF 433
RF 433 is also called a wireless transceiver module. It uses radio frequency technology and is composed of a single IC radio frequency front-end produced by all-digital technology and ATMEL’s AVR microcontroller. It is a micro transceiver that can transmit data signals at high speed. The wirelessly transmitted data is packaged and error-checked. ﹑Error correction processing.
The application scope of RF 433 technology includes wireless POS machines, PDAs and other wireless smart terminals, security, computer room equipment wireless monitoring, and access control systems. Transportation, meteorology, environmental data collection, smart communities, building automation, PLC, logistics tracking, warehouse inspection and other fields.
8.NFC
NFC is an emerging technology. Devices using NFC technology can exchange data when they are close to each other. It evolved from the integration of contactless radio frequency identification (RFID) and interconnection technology. By integrating on a single chip Integrate the functions of proximity card readers, proximity cards and point-to-point communication, and use mobile terminals to implement mobile payment, access control, identity recognition and other applications.
Near field communication technology realizes multiple functions such as electronic payment, identity authentication, ticketing, data exchange, anti-counterfeiting, advertising, etc. It changes the way users use mobile phones and makes users’ consumption behavior gradually become electronic.
9. UWB
UWB is a carrier-less communication technology that uses non-sinusoidal narrow pulses in nanoseconds to microseconds to transmit data. UWB was used for short-distance high-speed data transmission in the early days. In recent years, foreign countries have begun to use its sub-nanosecond ultra-narrow pulses for short-distance and precise indoor positioning.
Unlike traditional wireless systems such as Bluetooth and WLAN, which have relatively narrow bandwidths, UWB sends a series of very narrow low-power pulses over a wide frequency band. The wider spectrum, lower power, and pulsed data mean that UWB causes less interference than traditional narrowband wireless solutions and can provide performance comparable to wired in indoor wireless environments.
10.Modbus
Modbus is a serial communication protocol published by Modicon Corporation (now Schneider Electric) in 1979 for communication using programmable logic controllers. Modbus has become the industry standard for communication protocols in the industrial field and is now a commonly used connection method between industrial electronic equipment.
The Modbus protocol is a master/slave architecture protocol. There is a master node, and other nodes participating in communication using the Modbus protocol are slave nodes. Each slave device has a unique address. In serial and MB networks, only the node designated as the master can initiate a command.
There are many modems and gateways that support the Modbus protocol. Because the Modbus protocol is simple and easy to replicate, some of them are specifically designed for this protocol, but designers need to overcome some issues including high latency and timing.
“One carrot and one pit”, giving full play to their advantages in their respective application fields
Wireless communication technology is the most basic technology for realizing the Internet of Things and industrial automation in the future. With the growth of wireless applications, there will be more and more various technologies and equipment, and they will become increasingly dependent on wireless communication technology.
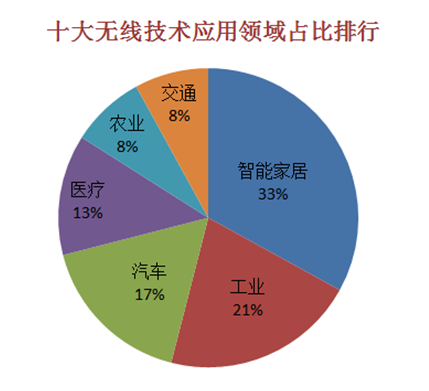

As listed above, each of the top ten wireless communication technologies has its own advantages and disadvantages, and is also limited by its own application scenarios. For example, Z-Wave technology has irreplaceable advantages in residential and lighting commercial control and status reading applications; Bluetooth and Wi-Fi have obvious cost and transmission characteristics, which have great advantages in common networking scenarios such as shopping malls, transportation and other places; The technical characteristics of Modbus determine that it is destined to be the first choice for communication in the industrial field, and its status is irreplaceable.
To realize the true Internet of Things, these technology alliances and personnel will need to work together and cooperate with each other in the future to support the huge global Internet of Things network.