RS232, RS422 and RS485 are commonly used serial communication standards in the communication field. Although all three standards can be used for serial communications, there are many differences between them. In this article, we will conduct a comprehensive analysis of the connections and differences between RS232, RS422 and RS485.
RS232

RS232 is one of the earliest standards in the field of serial communication. It defines the data transmission method, electrical characteristics and physical connection method. The RS232 standard is mainly used to connect two devices, such as a computer and a serial printer.
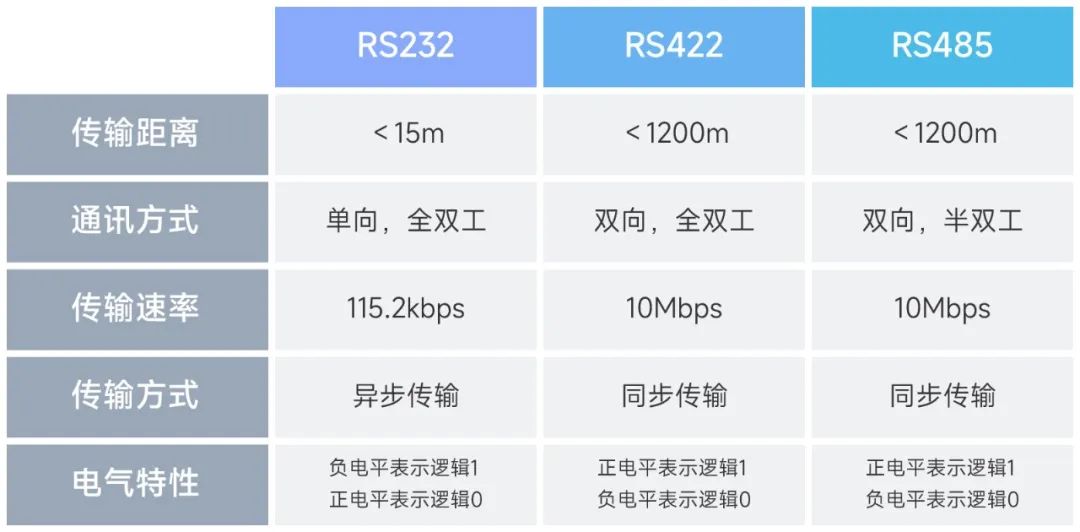
The transmission distance of RS232 is usually short, up to 15 meters only. In addition, RS232 also adopts a one-way communication method, that is, it can only transmit data in one direction, but cannot transmit data in two directions at the same time.
RS232 uses an asynchronous transmission method, that is, the data frame does not contain a clock signal, but the start bit and stop bit are used to determine the transmission timing of the data. In addition, RS232 also uses negative levels to represent logic 1 and positive levels to represent logic 0.
RS422
RS422 is a high-speed, long-distance serial communication standard that can support communication between multiple devices. The transmission distance of RS422 can reach 1200 meters. This is because it uses a differential signal transmission method, which can reduce the effects of electromagnetic interference and signal attenuation.
Different from RS232, RS422 adopts full-duplex communication method, that is, data can be transmitted in two directions at the same time. In addition, the data transmission rate of RS422 is also high, which can reach more than 10Mbps.
RS422 also uses a balanced transmission method, that is, the voltage of the data line to the ground line is equal, which can effectively reduce the impact of electromagnetic interference. In addition, RS422 also uses positive and negative logic representation, that is, positive level represents logic 1, and negative level represents logic 0.
RS485

RS485 is a serial communication standard that can support communication between multiple devices, similar to RS422. The transmission distance of RS485 can reach 1200 meters, but it uses half-duplex communication method, that is, data can only be transmitted in one direction.
Similar to RS422, RS485 also uses a differential signal transmission method, which can reduce the effects of electromagnetic interference and signal attenuation. In addition, RS485 also adopts a multi-master-slave structure, which can support communication between multiple master devices and multiple slave devices.
RS485 also uses a balanced transmission method, that is, the voltage of the data line to the ground line is equal, which can effectively reduce the impact of electromagnetic interference. Different from RS422, RS485 uses a two-wire system, that is, the data transmission lines are A line and B line, where A line is the positive pole and B line is the negative pole.
RS485 also has some differences in communication protocol. It adopts a synchronous transmission method, that is, the data frame contains a clock signal, which can accurately control the transmission timing of data. In addition, RS485 also supports a variety of communication protocols, such as MODBUS, Profibus, etc., with high flexibility and scalability.
Resumir
The main differences between RS232, RS422 and RS485 lie in transmission distance, communication method, transmission rate, transmission method and electrical characteristics.
RS232 is suitable for short-distance point-to-point communication; RS422 is suitable for long-distance and high-speed point-to-point or multi-point communication; RS485 is suitable for long-distance multi-point communication. In addition, RS485 also has the characteristics of half-duplex communication, synchronous transmission and multiple communication protocols, and has higher flexibility and scalability.
Therefore, in practical applications, choosing an appropriate serial communication standard requires considering the actual application scenarios and needs, and making judgments and selections based on various factors.