As technology continues to develop and advance, edge computing technology is also advancing with the times. As an important link between the physical world and the digital world, edge computing gateways are increasingly highlighting their unique value. In this article, we will distinguish between high and low-compatibility edge gateways from several different dimensions, such as hardware, features, and usage scenarios, to make reference basis for selecting edge gateways.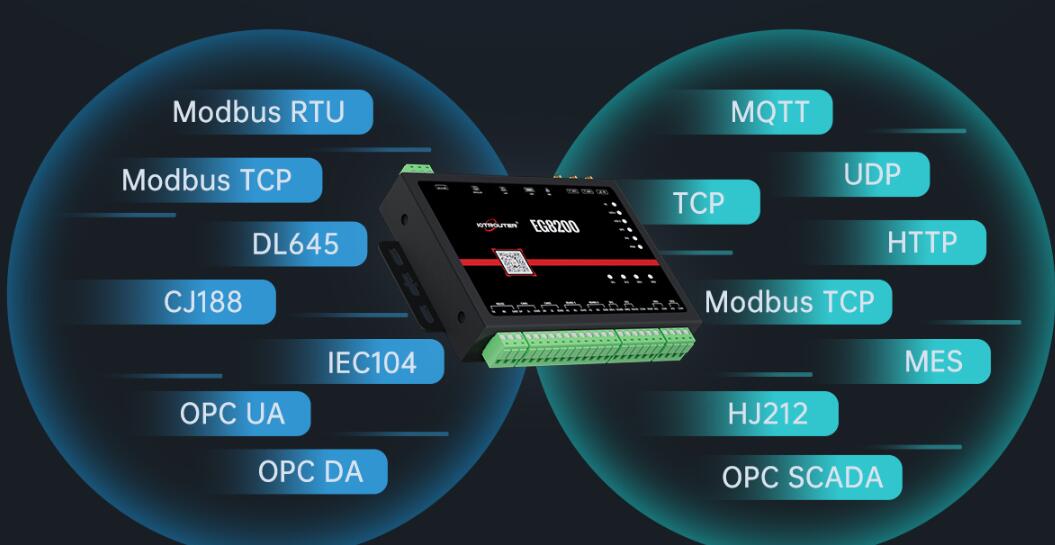
1. Hardware
Highly configurable edge gateways generally use high-performance processors, high-speed storage and high-capacity memory, and are also equipped with multiple network interfaces and expansion slots to meet the more complex needs of handling massive data and highly concurrent requests. Of course, higher hardware configurations also lead to higher prices for high-capacity edge gateways.
Lower-end edge gateways have lower processor configurations, lower storage speeds and less memory, fewer network interfaces, and even no expansion slots. Due to hardware constraints, low-profile edge gateways perform poorly overall in terms of performance.
2. Functionality
In terms of functionality, there is a very clear difference between a high-compatibility gateway de borda and a low-compatibility edge gateway. High-compatibility gateway de borda, such as EG8200 of IOTROUTER, is not only compatible with various mainstream PLC protocols, interfaces and third-party platforms, but also supports a variety of network access methods such as 4G, network port and wifi, and it can also automatically reconnect to a dropped line and intelligently switch backup. Not only that, the high gateway has a more powerful data processing capabilities, the sensor can be real-time data formatting, data processing, instructions issued and other functions, but also supports the secondary development of the gateway to better meet individual needs.
Low edge gateway is relatively simple, only supports some basic network connection and data transmission functions, while some advanced protocols and interface standards may not be able to support, data processing capabilities are relatively poor. If we only need the most basic data connection and transmission, then give priority to low-profile edge gateways, and if there are deeper functional requirements, then give priority to high-profile edge gateways.
3. Usage Scenarios
In large-scale scenarios such as smart cities, industrial automation, intelligent driving and other large-scale scenarios, massive data will be generated at any time, and at this time, high-compatibility edge gateways can play an advantage. Real-time processing of massive data, achieve high concurrency, provide compatibility communication ability, for the stable and efficient operation of industry applications to provide basic protection.
In scenarios such as smart home and environmental monitoring, which generally do not have high requirements for data processing and real-time, the low-provisioning edge gateway is more suitable. It can maintain low cost and power consumption while satisfying basic network connectivity and effective data transmission.
Consumers can find the most suitable edge gateway according to their own application requirements and specific usage scenarios when making decisions.