From an operator’s perspective, IoT can be divided into IoT in licensed spectrum (long range) and IoT in unlicensed spectrum (short range). The Internet of Things in unlicensed spectrum is very common, such as ETC, WIFI, Bluetooth, NFC, etc. Using unlicensed public frequency bands cannot form a wide area network and can only be used in local areas. The IoT in licensed spectrum is based on operator cellular network communication, with dedicated frequency bands, no interference, wide-area connections, universal equipment, roaming, and quality assurance.
Characteristics of IoT devices:
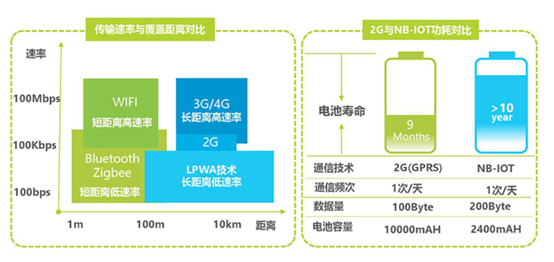
From the distance of communication distance, IoT communication technology can be divided into short-distance communication and long-distance communication.
Short-distance communication: WI-Fi, Bluetooth, ZigBee, Z-Wave, etc.
Long-distance communication: NB-IoT, eMTC, LoRa , Sigfox, etc.
The main difference between them is power consumption and distance. Similar to surfing the Internet on a mobile phone, using WI-Fi or data services. The coverage of WI-Fi is limited, while the data service network has full coverage. The power consumption of WI-Fi is also greater than that of data services.
Communication technologies such as NB-IoT, eMTC, LoRa, and Sigfox are also cellular communication technologies and can be classified into LPWA technology (Low Power Wide Area, Low Power Wide Area Network).
LPWA technology has longer coverage distance, lower power consumption, higher security and reliability, and can meet more industry applications.
With the diversification of IoT application scenarios, traditional “short-distance” IoT technology has shown certain shortcomings. The emergence of “long-distance” IoT technology has made up for these shortcomings and brought more room for development to the industry.


Cellular IoT devices actually have the following six major characteristics:
-
- Simple design: Low system complexity can ensure that IoT devices work normally in harsh environments.
- Low cost: IoT devices are generally low cost and large in volume.
- Large coverage: It is necessary to ensure that the data of some instruments and equipment in the basement can be transmitted.
- Low power consumption: Most application scenarios require the use of battery functions and need to be able to work for several years.
- Low rate: For example, in some meter reading applications, only a few dozen bytes need to be transmitted a day (this can only be understood as most low-speed scenarios, and only a few medium-high-speed scenarios).
- Massive device access.

Although there are many communication technologies used in the Internet of Things, no single technology has unified the world so far. It can only be said that each technology has its own advantages and disadvantages and its own application scenarios.