In this type of scenario, the environment is generally difficult, the facilities are simple, and the manpower for inspection and monitoring is relatively insufficient. Many accidents, such as forest fires, cannot be discovered and dealt with in time. There is an urgent need for unattended IoT means to achieve intelligent remote control. Supervision.
IoT applications in forest fire management and protection scenarios generally have the following characteristics:
(1) It is located in a remote location, requires simple and convenient engineering installation, and is sensitive to operation and maintenance costs;
(2) The territory is vast and access points are sparsely distributed, requiring the system to have wide-area coverage capabilities;
(3) Involving daily command and dispatch among multiple management teams, there is a rigid demand for voice communication and cluster dispatch functions.
In terms of network coverage, LoRa coverage is relatively small, so LoRa requires more base stations, the construction cost of the system is high, and the maintainability is low. The characteristics of the NB-IoT public network determine that it focuses more on the goals of optimal profitable business coverage and minimum comprehensive network construction costs. Therefore, it is difficult to achieve coverage in such remote uninhabited areas, let alone applications. P-IoT adopts a large-area technology system, which requires a small number of base stations to cover the same area, low network construction costs, and convenient daily operation and maintenance. It is very consistent with the application needs of forest defense wide-area non-coverage scenarios. In addition, P-IoT base stations can be co-located with dedicated digital cluster base stations, which not only saves a lot of infrastructure construction costs, but also meets users’ multiple needs for the Internet of Things, voice communications, and cluster scheduling. In terms of terminal power consumption, P-IoT IoT technology has greater power saving capabilities than other technologies. Through various methods such as lightweight protocol stack design, sleep mode design, and adaptive link technology, the power consumption of P-IoT terminals is at a low level, which greatly reduces the human operation and maintenance costs caused by frequent battery replacement during system operation. .
my country’s current forest prevention measures include:
(1) Publicity and education;
(2) Routine precautions mainly taken by forest rangers entering forest areas for patrolling;
(3) Manual inspection and management of wild fire sources in key periods and areas uniformly deployed by the Forest Defense Command;
(4) Establish fire-fighting and rescue teams, etc. According to feedback from a large number of front-line actual situations, it is difficult for limited forest rangers to patrol a large range of forest resources to achieve a wide range of patrol coverage. And the roads in most forest areas are in poor condition, so it takes a long time for rangers to reach each lookout tower. Traditional forest prevention measures based on manual inspection and monitoring cannot meet the needs of intelligent forestry supervision and inspection, whether in terms of inspection coverage or alarm timeliness.
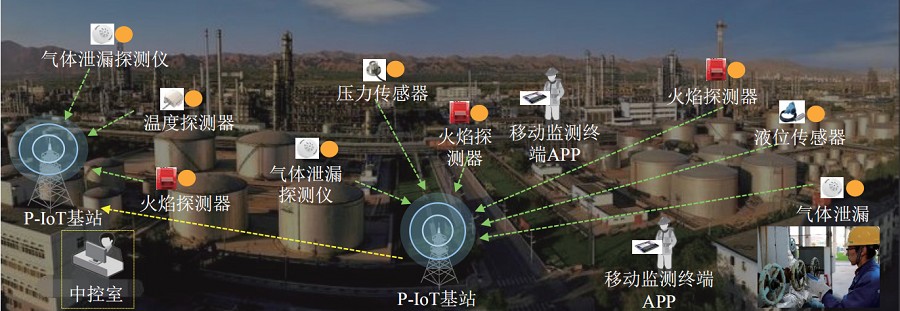
As shown in the figure above, various related data are obtained by deploying front-end sensing terminals, and the sensing data is transmitted back to the front command center through the P-IoT base station, and then transmitted to the rear command center through the Internet. With the help of the P-IoT system, forestry light monitoring, temperature and humidity monitoring, soil monitoring, meteorological and hydrological monitoring, insect monitoring, wildlife monitoring, personnel location monitoring, bayonet monitoring, ancient and famous tree monitoring, etc. can be carried out to achieve forest resource management. , forest fire prevention, natural forest protection, wind and sand prevention and forest pest control, intelligence, informatization and automation have greatly improved supervision efficiency and saved labor costs. While building P-IoT base stations in forestry to achieve wide-area coverage, unattended self-organizing network equipment can also be deployed. Self-organizing network equipment supports solar power, can be installed on poles or wall-mounted, and can be used as a backup or extension network for private networks. The forestry monitoring platform summarizes and analyzes a large amount of sensory data collected by P-IoT to provide commanders with panoramic information on disaster situations and assist commanders in making judgments and decisions, thereby ensuring timely evacuation of personnel and effective control of disaster situations.
Up to now, a P-IoT smart forestry system has been built in Qilian Mountain, Qinghai Province. According to customer needs, the system monitors more than 30 forestry indicators. At the same time, the system is also equipped with broadband self-organizing network equipment to provide a backhaul link for video data.
Рекомендуемая статья: Интернет вещей