ARM’s business model
●ARM is only responsible for designing ICs and selling its own design IP (copyright).
●ARM does not produce chips itself, but licenses design IP to other semiconductor manufacturers to produce chips.
●Strictly speaking, ARM is not a semiconductor manufacturer.
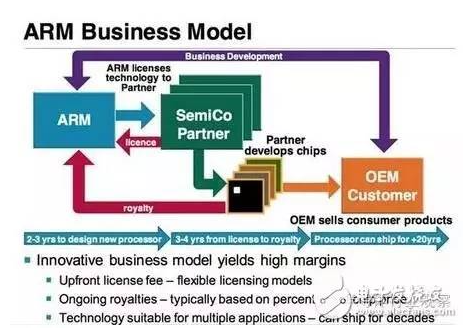
Unlike Intel, ARM is also a fabless semiconductor company. This is the same as NVIDIA and AMD after selling the wafer factory. However, ARM does not produce any processors itself. It mainly provides IP licenses to semiconductor partners ( Qualcomm, Apple, AMD and Samsung, etc.), the latter uses ARM’s architecture, design and development tools to launch its own processors, and then supplies them to OEM customers (this is the case for various mobile phone and tablet manufacturers). This is a simple For example, there may be a second authorization during the period.
ARM’s revenue comes from this cycle. Partners who purchase ARM’s IP license need to pay a technology licensing fee (license fee), and will also extract a certain amount of royalties (ongoing royalties, which can also be said to be commissions and franchise fees) based on the manufacturer’s processor price. etc.), which may involve all aspects of the chip.
To put it simply, ARM’s business model is “you pay, I authorize”. The design and development of processors is “teaching and meeting included”, and a series of tools will be provided to help customers simplify development.
ARM’s business model is very unique, at least now it is very different from the PC market. In the PC market, Intel dominates the development of the platform, and their products generally occupy the largest BOM material cost. In the smartphone and tablet market, most of the main processor costs are within 10% of the entire device. Generally, Generally speaking, they are single-digit shares. For example, the price of SoC processor in a US$400 device is generally US$15, and the share is 3.75%. Intel’s theory is that ultra-portable mobile devices will eventually change as chip complexity increases, but so far (and perhaps for some time in the future), the market still requires different business models.
How does ARM work?
As mentioned earlier, ARM’s main business model is to provide IP licensing. ARM also said that it can provide a variety of flexible licensing types. Specifically, there are three licensing methods: POP, processor and architecture licensing.
Processor licensing refers to authorizing a partner manufacturer to use ARM-designed CPU or GPU processors. The other party cannot change the original design, but can use it accurately according to its own needs. For example, Samsung’s Exynos 5 Octa uses four Cortex-A7 and four Cortex-A15 processors, which is processor authorization. ARM will provide a series of guidance to ensure that users use their designs, but in the end the frequency and power consumption of the product still depend on the manufacturer’s own team.
POP (processor optimization pack, processor optimization package) authorization is an advanced method of processor authorization. If the partner’s team cannot control the ARM processor, then ARM can also sell the optimized processor to you, so that users can Processes with guaranteed functions have been planned and produced using technology. In the Cortex-A8 era, Samsung and Apple teams were able to develop better processors than other companies, but not all companies have such capabilities, so POP licensing is more suitable for these companies that are willing but powerless.
The Cortex-A12 architecture released by ARM is a POP licensing method under the 28nm process of GF and TSMC.
The last authorization method is architecture authorization. ARM will authorize the other party to use its own architecture (ARMv7 or ARMv8), and then the other party can design the processor according to your own needs. This is the authorization method used by Qualcomm Krait processors. Apple now The same goes for the “Swift” architecture. These processors are ISA compatible with ARM’s own planned Cortex-A15 processor, but there are Qualcomm and Apple’s own implementation methods.
In this kind of authorization, you will get some guidance and a series of tests to verify compatibility with ARM ISA. ARM will provide some assistance, but it is impossible to help you design and develop your own processor.
How does ARM make money?
Intel, AMD and NVIDIA all make a living by selling processors. ARM does not sell any processors. It mainly relies on technology licensing fees and royalties. Manufacturers have to pay these two fees. Both of them are different in different processor architectures. The share is also different.
Technology licensing fees are charged based on the complexity of the chip architecture, and the old ARM11 is much cheaper than the latest Cortex-A57. Technology licensing fees are generally between US$1 million and US$10 million, although the actual situation may be higher or cheaper than these two figures.
Royalty commission is based on share. The typical share is 1-2%. If the company’s chips are sold externally, then the value is easy to calculate. If it is sold internally (such as Samsung’s self-produced and self-sold products), then the royalty rate is The share should also be calculated based on the market price.
Royalty share for different IPs
The above is the royalty share of ARM’s different IP licenses. Most of them are around 1-2%. The 0.5% share of POP licenses is not calculated based on the chip price. It is collected from the wafer factory. The calculation is 0.5% per wafer.
Generally speaking, it takes 6 months for both parties to sign a contract, and the distance from obtaining technical authorization to the first shipment that can generate revenue is as long as 3-4 years. Depending on different market conditions, manufacturers can continue to ship for about 20 years.
More than half of the 320 authorized manufacturers are paying royalties. Most of the other manufacturers are in the stage of signing licensing agreements and shipping products. ARM can add 30-40 new authorized manufacturers every year.
80% of the companies that signed licensing agreements sold the processors they designed on the market, and the other 20% were either acquired or failed for other reasons.
50% of ARM’s revenue comes from royalties, 33% is technology licensing fees, and the rest is software tools and technical support fees.
ARM’s operating conditions are good. In 2015, ARM achieved fruitful results. In addition to revenue of nearly US$1.5 billion, an increase of 15% over the previous year, in terms of the popular virtual reality VR, it was also due to the breakthrough of the Mali GPU developed by ARM for VR. The current technical limit will have brilliant market performance in the future. But considering that there are so many ARM designs now, ARM’s revenue is still relatively small, and ARM should consider increasing its royalty share. However, because of ARM’s unique business model, their gross profit margin is as high as 94%, and their operating profit is around 45%.
Authorization Types and Selection
Although the three main types of licenses provided by ARM have been mentioned earlier, the licenses provided by ARM are a series of complex ones.
Academic licenses are free, but you cannot sell processors of any size, but it is still good for learning architecture in universities or research institutes. DesignStart is also a low-cost licensing option, but of course you can’t sell the designed chips to make a profit.
For those situations where only a single application is required, ARM provides a Single Use license. A general Cortex-A grade CPU license only costs US$1 million and a 2% commission.
MuTIl-Use makes sense for large companies. Although you need to pay more license fees, you can use the CPU license in any product within a certain period (such as 3 years), unless the license expires, otherwise you It can be used on any product at will.
Subion license is one of the most interesting of several licensing methods. Customer companies can spend a sum of money to purchase a complete set of licenses from ARM. This kind of license is suitable for engineering managers who do not need to worry about the budget to develop a new chip development plan. Of course, the price is more money, and the technology license fee is $10 million level.
The top one is architecture authorization, which has been introduced before. Currently, 15 companies including Marvell, Qualcomm, and Apple have architecture authorization.
Another thing to mention is the three early-stage cooperative development partners selected by ARM. Since ARM itself does not sell any chip products, it needs to ensure that each generation of products has partners that release processors based on ARM’s latest and best architecture. Therefore, they will choose three manufacturers to cooperate closely. The purpose of selecting these manufacturers is As they expand the market, we tend to focus on high-end smartphone/tablet SoC processors, but ARM has also found their advantages in industrial applications, digital homes, smart TVs, and other markets.
The three selected partners can obtain earlier processor architecture information than other authorized manufacturers. They help with testing and debugging, and even provide direct feedback to ARM. The advantage they gain is that they have a better market advantage than other companies.
Keywords in this article: data transmission terminal, GPRS DTU, GPRS RTU