What is baud rate
Baud rate is the term used to describe the number of bits transmitted per second in digital communications. It is usually expressed as “Baud” or “Baud”, but may also be expressed as symbols per second or frames transmitted per second.
In serial communications, each bit or symbol represents the state of a voltage or current. Baud rate represents the number of bits or symbols transmitted per second. For example, a serial communication interface with a baud rate of 9600 can transmit 9600 bits or symbols per second. The higher the baud rate, the faster the data transfer speed.
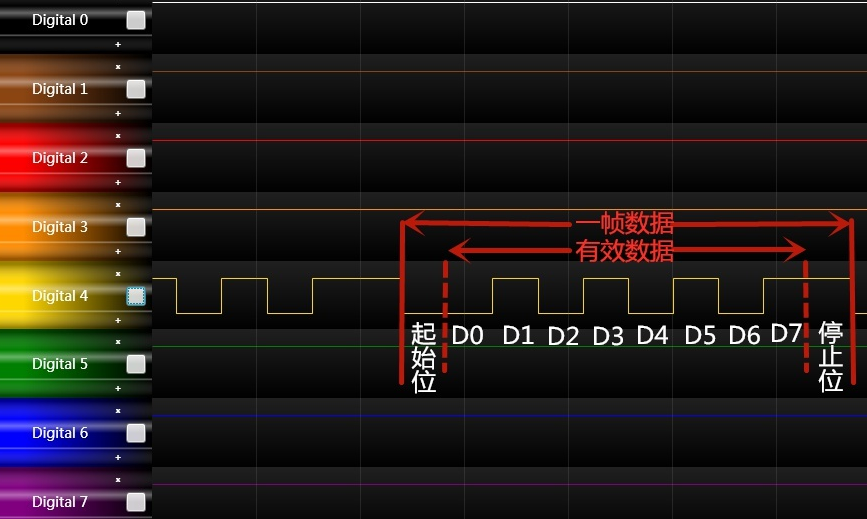
It is important to note that baud rate and data transfer speed are not exactly the same. Baud rate simply represents the number of symbols transmitted per second, while data transmission speed is also affected by many other factors, such as the number of data bits, parity, start and stop bits, etc.
In digital communications, baud rate is a very important parameter because it determines the speed and reliability of communication. If the baud rate is set incorrectly, data transmission errors or failures may occur. Therefore, when configuring a serial communication device, you must ensure that the baud rate is set correctly and matches the other device to ensure normal data transmission.
what is bitrate
Bit rate is a term used to describe the rate at which a digital signal is transmitted, usually expressed as the number of bits transmitted per second. Bit rate is commonly used in digital communication systems such as computer networks, digital audio and video transmission, etc.
The higher the bitrate, the faster the data transfer speed. For example, an Ethernet connection with a bit rate of 100 Mbps (megabits per second) can transmit 100 megabits of data per second, while a connection with a bit rate of 1 Gbps (gigabits per second) can transmit even faster speed.
It’s important to note that bitrate generally does not equate to data transfer speed. Because data transmission usually contains other bits besides data bits, such as start and stop bits, parity bits, etc. Bitrate simply represents the number of bits transferred per second, and the actual data transfer speed takes these extra bits into account.
In digital communications, bit rate is an important parameter as it determines the speed and reliability of data transmission. When setting the bit rate, you need to choose an appropriate bit rate based on system requirements, communication media, and other factors. If the bitrate is set incorrectly, it can cause data transfer errors or failures.
The connection between baud rate and bit rate
Baud rate and bitrate are both terms that describe the speed of digital communication, but they have slightly different meanings.
Baud rate is commonly used in serial communications to describe the number of symbols (usually data bits) transmitted per second. For example, if a serial communication interface has a baud rate of 9600, it means that it can transmit 9600 data bits per second.
Bit rate is commonly used in parallel communications to describe the number of bits transmitted per second. For example, if an Ethernet connection has a bit rate of 100 Mbps, it means it can transmit 100 megabits of data per second.
Although baud rate and bit rate have slightly different meanings, there is a direct relationship between them. In serial communications, the higher the baud rate, the more bits are transmitted per second because each symbol typically contains multiple bits. For example, a serial communications interface with a baud rate of 9600 can transmit 9600 symbols per second. Each symbol typically contains 8 bits, so it can transmit 9600 x 8 = 76,800 bits per second. Therefore, in serial communications, the baud rate can be used to estimate the number of bits transmitted per second.
It is important to note that baud rate and bit rate are not exactly the same terms, so in communications, it is important to use the correct terminology to avoid confusion.